Trading in financial markets offers a variety of approaches, each tailored to different goals, risk tolerances, and time commitments. Understanding different trading styles is important for anyone looking to walk through the complex world of trading. From the rapid-fire pace of scalping to the long-term strategies of position trading, each style has its unique characteristics and advantages.
This article will explore the four primary trading styles (scalping, day trading, swing trading, and position trading) providing insights into how they work and helping you determine which one aligns best with your trading objectives and lifestyle. Whether you’re a beginner trader or someone looking to refine your strategy, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and optimize your trading performance.
Table of Contents
What Is Trading Style?
Trading styles refer to the various approaches traders use to buy and sell financial instruments. In simple terms, a trading style refers to the approach or strategy a trader adopts to enter and exit trades in the financial markets. Also, each trading style has its unique characteristics, timeframes, and risk profiles. By choosing a trading style, you are essentially defining your approach to trading and the time and effort you are willing to commit.
Trading styles can be molded to fit a trader’s time restrictions, profit goals, and personal strengths. While most traders share the same goals, they achieve these goals using a variety of different trading styles. There is not one trading style that is better than any of the others. What typically separates the trading styles is the length of time you intend to be in a trade, the timing of your entry, and in some cases, the frequency of the trades.
Importance of Choosing the Right Trading Style
Choosing a trading style that fits your personal circumstances, goals, and market conditions can significantly enhance your trading success and overall experience. So, there are several reasons for why choosing the right trading style is important:
- Alignment with Goals: Different trading styles cater to different financial goals. For example, scalping might be suitable for those seeking quick, small profits, while position trading is better for long-term growth.
- Risk Tolerance: Each trading style comes with its own risk profile. Day trading involves high risk due to frequent trades, whereas position trading might be less risky but requires patience.
- Time Commitment: Some styles, like day trading and scalping, require constant monitoring of the markets, while others, like swing or position trading, are less time intensive.
- Psychological Comfort: Your trading style should match your psychological comfort level. High-frequency trading can be stressful, while long-term investing might be more relaxed.
- Resource Availability: Different styles require different resources. Scalping needs advanced software and technical knowledge, while swing trading might only need basic charting tools.
- Market Conditions: Certain styles perform better under specific market conditions. For instance, momentum trading works well in trending markets, while range trading is effective in sideways markets.
Trading styles can vary widely, catering to different trader preferences and goals. Let’s explore some of the most common trading styles:
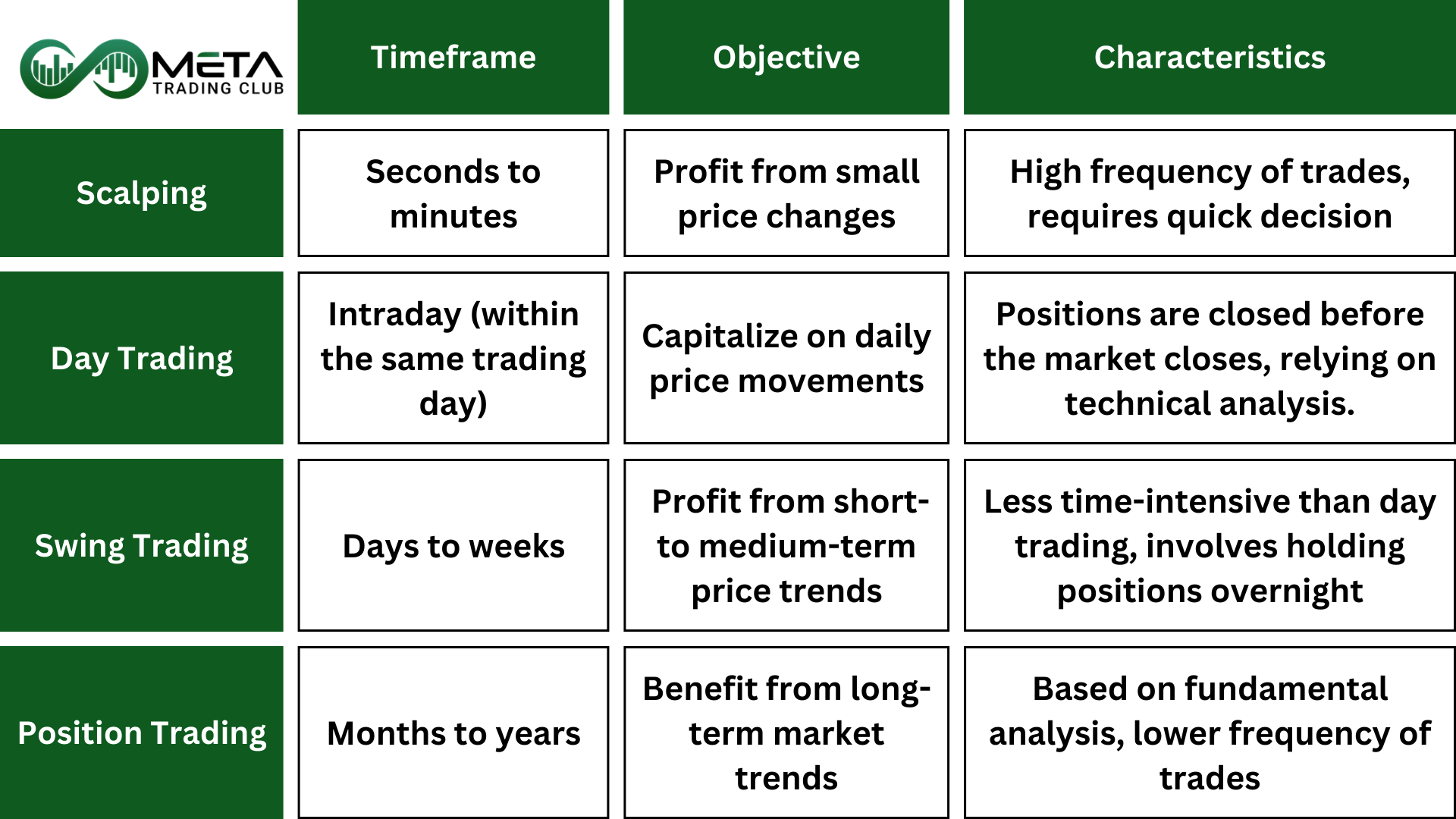
Day trading
A day trader is a type of trader who buys and sells financial instruments within the same trading day, aiming to profit from short-term price movements.
Key Features of Day traders
- Intraday Trading: Day traders open and close all their positions within the same trading day. They do not hold positions overnight to avoid the risks associated with after-hours price movements.
- High Volume of Trades: Day traders execute a large number of trades each day to capitalize on small price fluctuations. This requires a high level of activity and quick decision-making.
- Leverage: Many day traders use leverage to amplify their returns. Leverage allows them to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital, but it also increases the potential for significant losses.
- Technical Analysis: Day traders rely heavily on technical analysis, using charts, patterns, and indicators to predict short-term price movements. They focus less on fundamental analysis, which is more relevant for long-term investments.
- Market Efficiency: Day traders aim to exploit market inefficiencies, such as temporary supply and demand imbalances, to make profits. They often use strategies like momentum trading, scalping, and arbitrage.
Tools
- Trading Platforms: High-speed brokers and platforms are essential for executing trades quickly in day trading.
- Charts and Indicators: Real-time charts with indicators like moving averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index), and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) help identify trading opportunities.
- News Feeds: Real-time news services like Bloomberg and Reuters provide crucial information that can impact market movements.
Strategies
- Scalping: This involves making numerous small trades to capture tiny price movements. For example, a trader might buy a stock at $50.00 and sell it at $50.05, repeating this process multiple times.
- Momentum Trading: Traders look for stocks showing strong price movements and trade in the direction of the trend. For instance, if a stock is rapidly increasing in price due to positive news, a trader might buy in and ride the wave.
- Breakout Trading: This strategy involves entering trades when the price breaks through key levels of support or resistance. For example, if a stock breaks above a resistance level of $100, a trader might buy, anticipating further upward movement.
Benefits
- Quick Profits: Day traders can capitalize on intraday price movements. For example, if a stock opens at $100 and rises to $105 within the day, a day trader can profit from this $5 increase.
- No Overnight Risk: By closing all positions before the market closes, day traders avoid risks associated with overnight news or events that could impact prices.
- High Liquidity: Day traders often trade highly liquid stocks or instruments, ensuring they can enter and exit positions quickly without significant price slippage.
Risks
- High Stress: Constant monitoring of the markets and making rapid decisions can be stressful. For instance, a sudden market downturn can require immediate action to cut losses.
- Transaction Costs: Frequent trading incurs high transaction costs, including commissions and spreads. These costs can eat into profits if not managed carefully.
- Emotional Strain: The fast-paced nature of day trading can lead to emotional exhaustion, impacting decision-making and overall mental health.
Traits of Successful Day Trader
- Discipline: Sticking to a trading plan and not deviating based on emotions. Day traders must execute trades according to their strategy without hesitation.
- Quick Decision-Making: Ability to make rapid decisions based on real-time data. This is crucial for capitalizing on short-term price movements.
- Emotional Control: Managing emotions like fear and greed to avoid impulsive decisions. Staying calm under pressure is essential.
- Focus: Maintaining intense focus throughout the trading day to monitor multiple trades and market conditions.
A disciplined day trader will set strict entry and exit points and adhere to them, even if the market becomes volatile.
Swing Trading
A swing trader is a type of trader who seeks to capture short- to medium-term gains in a financial instrument over a period of a few days to several weeks. Also, swing trading can be a rewarding approach for those who prefer a balance between short-term and long-term trading. However, it requires a good understanding of technical analysis, market conditions, and risk management.
Key Features of Swing traders
- Holding Period: Swing traders hold positions longer than day traders but shorter than long-term investors. Typically, positions are held from a few days to several weeks.
- Technical Analysis: Swing traders primarily rely on technical analysis to identify trading opportunities. They use charts, patterns, and technical indicators to predict future price movements.
- Fundamental Analysis: While technical analysis is the primary tool, some swing traders also consider fundamental analysis to understand the broader context of the market or specific securities.
- Market Conditions: Swing trading can be effective in various market conditions, including trending and range-bound markets. The goal is to capture a portion of the expected price move.
Tools
- Technical Analysis Software: Tools like TradingView and StockCharts provide advanced charting capabilities.
- Indicators: Fibonacci retracement, Bollinger Bands, and MACD are commonly used to identify potential entry and exit points.
- Screeners: Stock screeners help identify stocks that meet specific criteria, such as price patterns or volume changes.
Strategies
- Trend Following: Swing traders look for established trends and enter trades in the direction of the trend. For example, if a stock has been steadily rising, a trader might buy and hold until signs of a reversal appear.
- Reversal Trading: This involves identifying potential trend reversals and trading against the current trend. For instance, if a stock has been declining but shows signs of bottoming out, a trader might buy in anticipation of a reversal.
- Pattern Trading: Traders use chart patterns like head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, and triangles to predict future price movements. For example, a head and shoulders pattern might indicate a potential reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend.
- Breakout Trading: Swing traders look for price breakouts from key levels of support or resistance. They enter trades when the price breaks out and aim to capture the subsequent price movement.
Benefits
- Flexibility: Swing trading allows for a more balanced lifestyle compared to day trading. Traders can analyze markets in the evenings and place trades that last several days or weeks.
- Larger Price Moves: Swing traders aim to capture significant price movements. For example, buying a stock at $50 and selling it at $60 over a week.
- Technical Analysis: Swing traders rely on technical analysis, which can be more predictable over short to medium terms. Patterns like head and shoulders or double tops/bottoms provide clear entry and exit signals.
- Potential for Higher Returns: By capturing larger price movements over several days or weeks, swing traders can potentially achieve higher returns compared to day trading
- Diversification: Swing traders can diversify their portfolio by holding multiple positions across different assets or markets
Risks
- Overnight Risk: Holding positions overnight exposes traders to risks from after-hours news or events. For instance, a negative earnings report released after market close can lead to a gap down in price.
- Market Volatility: Sudden market changes can negatively impact positions. A geopolitical event or unexpected economic data release can cause significant price swings.
- Requires Patience: Trades may take days or weeks to play out, requiring patience and discipline to stick to the trading plan.
- Emotional Discipline: Swing trading requires emotional discipline. Also, traders must stick to their trading plan and avoid impulsive decisions based on short-term market fluctuations.
Traits of Successful Swing trader
- Patience: Waiting for the right trading opportunities and allowing trades to develop over days or weeks. Patience helps in avoiding premature exits.
- Analytical Skills: Using technical analysis to identify trends and patterns. Swing traders need to analyze charts and indicators effectively.
- Adaptability: Adjusting strategies based on market conditions. Swing traders must be flexible to switch between bullish and bearish strategies.
- Risk Management: Setting appropriate stop-loss levels to protect against significant losses and managing risks.
A patient swing trader might wait for a stock to reach a key support level before entering a trade, ensuring a higher probability of success.
Scalp Trading
A scalper trader is a type of day trader who specializes in executing a high volume of trades to profit from small price movements. Scalping is a trading strategy focused on making numerous trades throughout the day to capture small price changes. Scalpers aim to profit from these minor fluctuations by entering and exiting trades quickly, often within seconds or minutes.
Scalper trading is a demanding but potentially rewarding strategy that requires a combination of speed, discipline, and technical expertise. By capitalizing on small price movements and executing a high volume of trades, scalpers aim to achieve consistent profits over time.
Key Features of Scalpers
- High Frequency of Trades: Scalpers may execute dozens or even hundreds of trades in a single trading session.
- Small Profit Margins: Each trade typically yields a small profit, but the cumulative effect of many successful trades can be substantial.
- Short Holding Periods: Scalpers hold positions for very short durations, minimizing exposure to market risks.
- Leverage Usage: To amplify returns, scalpers often use leverage, which allows them to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital.
Tools
- High-Speed Trading Platforms: Platforms with low latency, such as NinjaTrader, are essential for executing trades quickly.
- Charts and Indicators: Scalpers rely heavily on technical analysis, using short-duration charts (e.g., 1-minute, 5-minute) and indicators like moving averages, Bollinger Bands, and the Relative Strength Index (RSI).
- Direct Market Access (DMA): Access to real-time market data and direct market access is crucial for executing trades quickly and efficiently.
- Automated Trading Systems: Some scalpers use algorithmic trading systems to automate their strategies and execute trades at high speeds.
- Tick Charts: Charts that show price changes for every second provide sufficient data for making quick decisions.
Strategies
- Spread Trading: Profiting from the bid-ask spread involves buying at the bid price and selling at the ask price. For example, if the bid price is $50.00 and the ask price is $50.05, a scalper might buy at $50.00 and sell at $50.05.
- Order Flow Analysis: Analyzing the flow of buy and sell orders helps scalpers anticipate short-term price movements. For instance, a surge in buy orders might indicate an imminent price increase.
- High-Frequency Trading: Using algorithms to execute trades in milliseconds allows scalpers to capitalize on tiny price movements. For example, an algorithm might detect a small price discrepancy and execute a trade to profit from it.
Benefits
- Frequent Opportunities: Scalpers find numerous trading opportunities throughout the day, profiting from small price movements. For example, buying at $50.00 and selling at $50.05 multiple times.
- Small Profits: Consistent small profits can add up over time. Scalpers aim for high win rates with small gains per trade.
- High Liquidity: Scalping focuses on highly liquid markets, ensuring ease of entry and exit without significant price impact.
Risks
- High Transaction Costs: Frequent trades lead to high transaction costs, including commissions and spreads. These costs can significantly reduce overall profitability.
- Intense Focus: Scalping requires intense focus and quick decision-making. Missing a trade by a few seconds can mean missing the profit opportunity.
- Emotional Strain: The fast-paced nature of scalping can lead to emotional exhaustion, impacting decision-making and overall mental health.
- Market Volatility: Sudden market movements can result in losses, especially when using leverage.
Traits of Successful Scalpers
- Discipline: Scalpers must strictly adhere to their trading plans and set daily loss limits to avoid significant losses.
- Precision: Executing trades with high accuracy to capture small price movements. Scalpers need to be precise in their entry and exit points.
- Speed: Making quick decisions and executing trades rapidly. Speed is crucial for taking advantage of tiny price changes.
- Concentration: Maintaining intense concentration to monitor the market continuously. Scalpers must stay alert to identify and act on opportunities.
- Risk Aversion: Implementing strict risk management to avoid significant losses. Scalpers use tight stop-loss orders to protect their capital.
A precise scalper might use Level II quotes to identify the best bid and ask prices, executing trades within seconds to capture small profits.
Position Trading
A position trader is a type of trader who holds positions in financial instruments for an extended period, ranging from several weeks to years. This trading style is based on long-term trends and market fundamentals.
Moreover, position trading involves buying and holding investments over a long period to capitalize on significant price movements. Unlike day traders or scalpers, position traders are less concerned with short-term market fluctuations and focus on the overall trend.
Position trading is a strategy suited for those who prefer a long-term approach to investing. By focusing on fundamental and technical analysis, position traders aim to capitalize on significant market trends. This strategy requires patience, discipline, and a thorough understanding of market dynamics.
Key Features of Position Traders
- Long Holding Periods: Position traders hold their investments for weeks, months, or even years, aiming to benefit from long-term trends.
- Trend Following: They identify and follow major market trends, buying assets expected to appreciate over time.
- Fundamental Analysis: Position traders rely heavily on fundamental analysis, evaluating economic indicators, company performance, and industry trends to make informed decisions.
- Technical Analysis: While fundamental analysis is primary, technical analysis is also used to determine optimal entry and exit points.
Tools
- Fundamental Analysis Tools: Analyzing financial statements, earnings reports, and other fundamental data is crucial for long-term investments.
- Economic Calendars: Tracking economic events and announcements helps position traders understand the broader market context.
- Long-term Charts: Weekly or monthly charts are used to analyze long-term trends.
Strategies
- Buy and Hold: This strategy involves holding positions for extended periods based on fundamental analysis. For example, an investor might buy shares of a company with strong growth prospects and hold them for several years.
- Sector Rotation: Traders move investments between sectors based on economic cycles. For instance, during an economic expansion, they might invest in cyclical sectors like technology and consumer discretionary.
- Dividend Investing: Focusing on stocks with strong dividend yields provides a steady income stream. For example, an investor might buy shares of a company with a history of consistent dividend payments.
Benefits
- Long-Term Gains: Position traders can benefit from long-term trends. For example, investing in a growing tech company and holding the stock for several years can yield substantial returns.
- Less Time-Intensive: Position trading requires less frequent monitoring, making it suitable for those with other commitments. Traders can review their positions weekly or monthly.
- Fundamental Analysis: Relying on fundamental analysis, position traders can make informed decisions based on a company’s financial health, industry position, and economic conditions.
Risks
- Market Downturns: Long-term positions can be heavily impacted by market downturns. For instance, a recession can led to significant declines in stock prices.
- Opportunity Costs: Holding positions for a long time can tie up capital, potentially missing out on other short-term opportunities.
- Patience Required: Requires a long-term perspective and patience to withstand market fluctuations and hold positions through volatile periods.
- Economic Changes: Changes in economic conditions or unexpected events can impact long-term trends.
Traits of Successful Position Traders
- Long-Term Vision: Focusing on long-term trends and fundamental analysis. Position traders need to see the bigger picture and not be swayed by short-term fluctuations.
- Research-Oriented: Conducting thorough research on companies, industries, and economic conditions. This involves analyzing financial statements and market trends.
- Resilience: Withstanding market downturns and holding positions through volatility. Resilience helps in maintaining confidence in long-term investments.
- Strategic Planning: Developing and sticking to a long-term investment strategy.
- Discipline: Sticking to a well-defined trading plan and not reacting to short-term market noise is crucial.
- Analytical Skills: Strong analytical skills are essential for evaluating market trends and making informed decisions.
A research-oriented position trader might invest in a company with strong growth prospects and hold the stock for several years, benefiting from long-term appreciation.
How to Choose the Trading Style?
Choosing the right trading style depends on several factors, including your personality, lifestyle, risk tolerance, and financial goals. Here are some steps to help you determine the best trading style for you:
1. Assess Your Personality
- Risk Tolerance: Are you comfortable with high-risk, high-reward scenarios, or do you prefer more stable, long-term investments?
- Decision-Making: Do you make decisions quickly and confidently, or do you prefer to take your time and analyze thoroughly?
- Patience: Are you patient enough to wait for long-term gains, or do you prefer quick results?
2. Evaluate Your Lifestyle
- Time Commitment: How much time can you dedicate to trading each day? Day trading requires full-time attention, while swing and position trading can be more flexible.
- Work Schedule: Do you have a regular job or other commitments that limit your trading hours?
- Stress Levels: Can you handle the stress of constant market monitoring, or do you prefer a more relaxed approach?
3. Define Your Financial Goals
- Short-Term vs. Long-Term: Are you looking to make quick profits, or are you focused on building wealth over the long term?
- Income Needs: Do you need regular income from trading, or can you afford to wait for long-term capital appreciation?
- Capital Available: How much capital do you have to invest? Some trading styles, like scalping, may require more capital due to frequent trades and transaction costs.
4. Understand the Different Trading Styles
- Day Trading: Suitable for those who can dedicate full-time hours, handle high stress, and make quick decisions.
- Swing Trading: Ideal for those who can spend a few hours each day analyzing markets and prefer holding positions for days to weeks.
- Position Trading: Best for those with a long-term perspective, patience, and the ability to conduct thorough fundamental analysis.
- Scalping: Fits those who thrive in fast-paced environments, can make rapid decisions, and have access to high-speed trading platforms.
5. Try Different Styles
- Paper Trading: Use a demo account to practice different trading styles without risking real money. This helps you understand which style suits you best.
- Backtesting: Test your strategies on historical data to see how they would have performed in the past.
6. Seek Education and Mentorship
- Courses and Books: Invest in educational resources to learn about different trading styles and strategies. Participate in our incubator program.
- Mentorship: Find a mentor or join a trading community to gain insights and advice from experienced traders.
7. Reflect and Adjust
- Self-Assessment: Regularly assess your performance and comfort level with your chosen trading style.
- Adaptability: Be willing to adjust your style as you gain more experience and as market conditions change.
Choosing the right trading style is a personal decision that requires self-awareness and a clear understanding of your goals and constraints. By following these steps, you can find a trading style that aligns with your strengths and preferences.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Trading Style
Choosing the right trading style is crucial for your success and satisfaction as a trader. Here are some key factors and considering these factors can help you choose a trading style that aligns with your goals, resources, and personal preferences.
1- Time Commitment
- Scalping and day trading require significant time and attention throughout the trading day.
- Swing and position trading are more suitable if you have limited time, as they involve less frequent monitoring.
2- Risk Tolerance
- Scalping and day trading have higher risk due to frequent trades and potential for rapid losses.
- Swing and position trading have lower risk, but still subject to market volatility.
3- Capital Requirements
- Scalping and day trading often require higher capital to cover frequent trades and potential losses.
- Swing and position trading can be started with lower capital, but still need sufficient funds to manage positions.
4- Market Knowledge and Experience
- Scalping and day trading require a deep understanding of technical analysis and market behavior.
- Swing and position trading benefit from a mix of technical and fundamental analysis.
5- Personality and Lifestyle
- Scalping and day trading are best for those who enjoy fast-paced environments and can handle stress.
- Swing and position trading are suitable for those who prefer a more relaxed approach and can be patient.
6- Trading Goals
- Scalping and day trading aim for quick, small profits that accumulate over time.
- Swing and position trading focus on capturing larger price movements over longer periods.
Final Words
Selecting the right trading style is a personal decision that hinges on various factors including your time commitment, risk tolerance, capital, market knowledge, personality, lifestyle, and trading goals. Each trading style offers unique advantages and challenges.
Scalping and Day Trading are suited for those who thrive in fast-paced environments and can dedicate significant time to monitoring the markets. Also, Swing and Position Trading are ideal for traders who prefer a more relaxed approach and can be patient with their investments.
Ultimately, the best trading style for you is one that aligns with your personal preferences, financial goals, and lifestyle. It’s important to thoroughly understand each style and consider how it fits into your overall trading strategy. By doing so, you can enhance your chances of success and enjoy a more fulfilling trading experience.
The four main trading styles are: scalping, day trading, swing trading, position trading.
Choosing a trading style depends on: time commitment, risk tolerance, experience level, market knowledge, personal goals.
Profitability depends on the trader’s skill, strategy, and market conditions. scalping is potential for small, frequent profits. Also, day trading could be profitable with quick decision-making. However, position trading could be profitable for long-term trends. But No single style guarantees the most profit; it varies per individual.
Swing trading is often recommended for beginners. It allows for more time to make decisions compared to day trading. Also it causes lower stress than scalping.
Yes, you can day trade with $1,000. However, you should use stop-loss orders to limit losses. Also, be cautious with leverage and broker fees. In addition, stick to a well-defined trading strategy.