In the world of trading, a stop loss serves as your financial safety net. It’s a predetermined price level at which you decide to exit a trade. When the market moves against your position, the stop order triggers an automatic trade, limiting potential losses. Whether you’re an experienced trader or a beginner, understanding stop loss strategies is essential for risk management.
Table of Contents
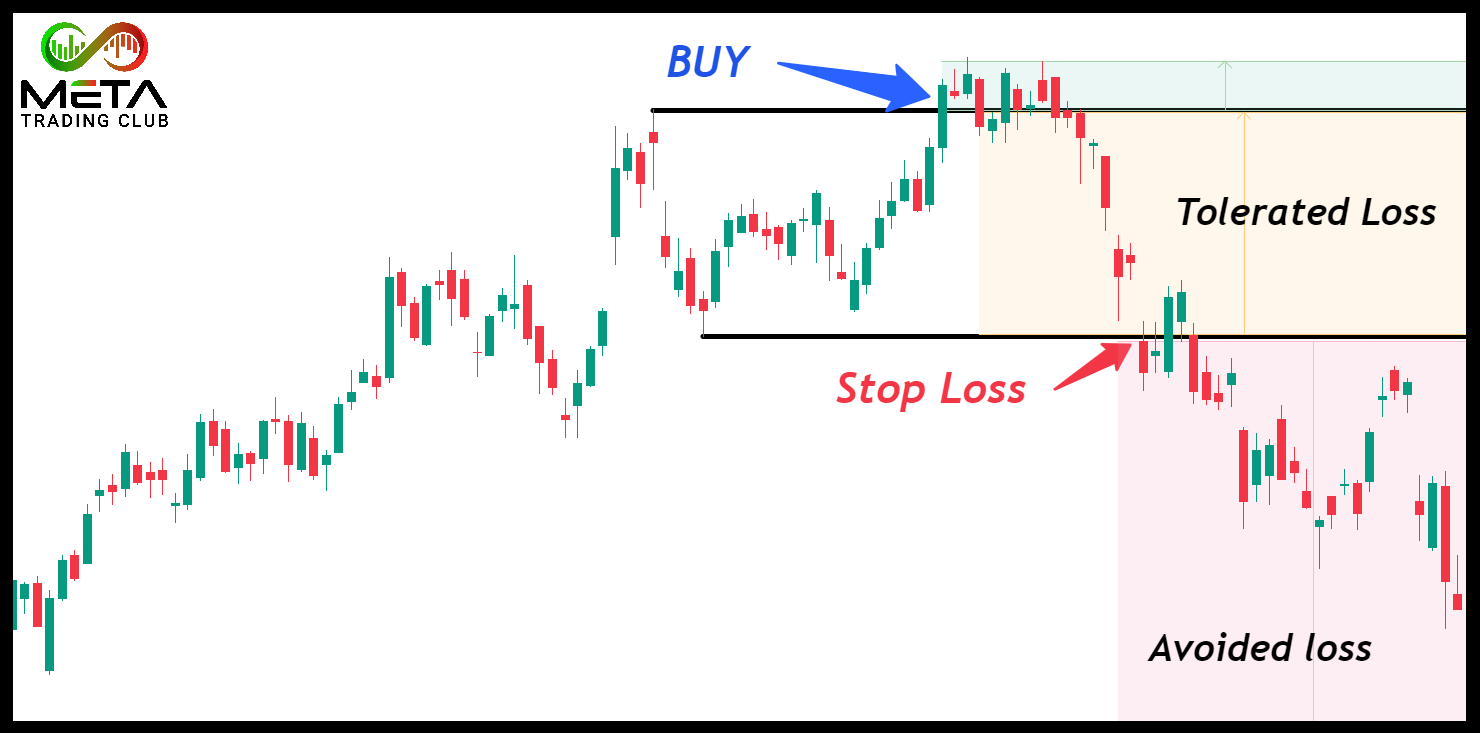
What Is Stop Loss?
A stop loss is a type of order that traders use to limit their potential losses in the financial market. Also, stop loss order is a market order that helps manage risk by closing your position once the asset reaches a certain price. However, this order aims to limit a trader’s losses on a position. If you set a stop loss order for 10% below the buy price, it will limit your losses to 10%. This helps in maintaining discipline and sticking to trading goals and strategies even in a volatile market condition.
Most of our decisions are based on our emotions but in trading, these emotions can mean financial ruin. Stop orders can help traders manage these emotions and avoid making impulsive decisions based on fear or greed. By setting a predetermined exit point, you can reduce the emotional stress of monitoring your trades and make rational decisions based on your trading plan.
Example
When you buy a stock or any other security, you can set a stop loss order. This order specifies a trigger price at which you want to sell the security. For example, if you buy shares of Apple at $200 per share, you might set a stop loss at $190. This means that if the stock price drops to $190 or below, your stop loss order will activate. When the stop order becomes active. Then the brokerage platform automatically executes the order by selling your shares at the prevailing market price. This helps protect you from further losses if the stock continues to decline.
These stop orders are essential for risk management. They prevent emotional decision-making during market volatility. Without a stop loss, you might hold onto a losing position, hoping it will recover. But if the stock keeps dropping, your losses could become substantial.
How Does Stop Loss Order Work?
A stop loss order is a tool used by traders to limit potential losses or lock in profits on an existing position. It’s designed to limit potential losses by automatically triggering an order to close the trade if the price moves against your position. Also, these orders help protect your capital by limiting potential losses. They’re especially useful when you can’t monitor your trades constantly. Here’s how it works:
For example, if you own a stock currently trading at $100, you might set a stop loss order at $90. As the market fluctuates, the price of the stock may rise or fall. If the stock price falls to $90, your stop order is triggered. Once the stop price is reached, the stop loss order becomes a market order. This means it will be executed at the next available price. In a fast-moving market, the execution price might be slightly different from the stop price due to slippage. The trade is completed, and the stock is sold, helping you limit your losses.
Also, these orders can also be used to protect short positions. In this case, you set the stop price above the current market price, and if the price rises to that level, the position is closed through an offsetting purchase. Hence, stop loss orders are essential tools for managing risk and protecting your trades from significant declines. They can be particularly useful in volatile markets.
How to Set Stop Loss?
Setting an appropriate stop loss level is crucial for managing risk in your trades . Here are some methods you can consider:
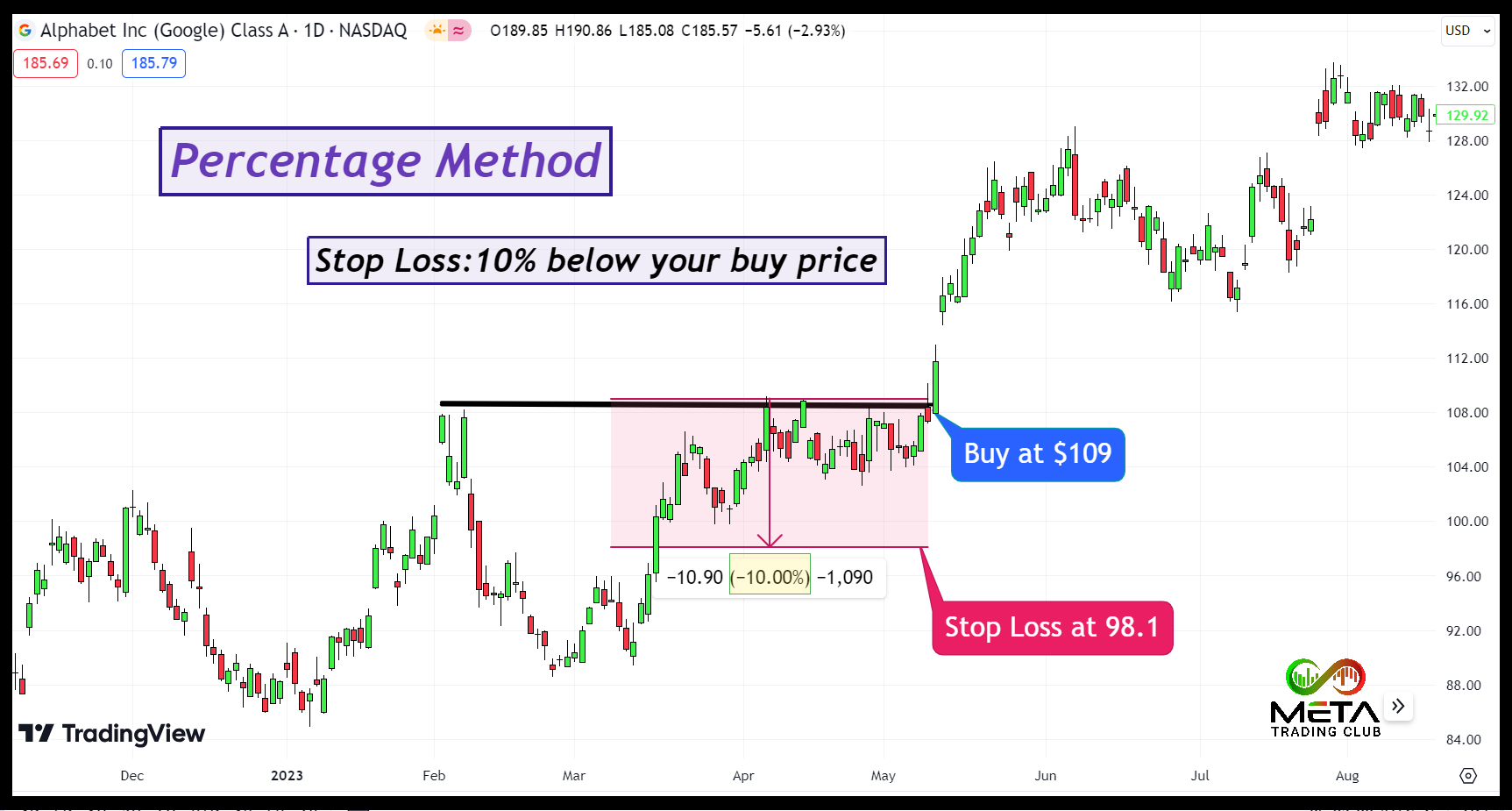
Percentage Method
The Percentage Method for setting a stop loss is a straightforward and popular approach among traders. Here’s how you can use this approach:
- Determine the percentage: Decide on the percentage of the stock price you are willing to lose before exiting the trade. This percentage represents your risk tolerance.
- Calculate the stop loss price: Multiply the current stock price by the chosen percentage. Subtract this value from the current stock price to get your stop price.
For example, if you own a stock trading at $109 per share and you are comfortable with a 10% loss, you can set your stop loss at $98.1 ($109 – ($109 * 0.10)).
This method is simple and helps you manage risk by limiting potential losses to a predefined amount. It’s particularly useful for maintaining discipline in your trading strategy.
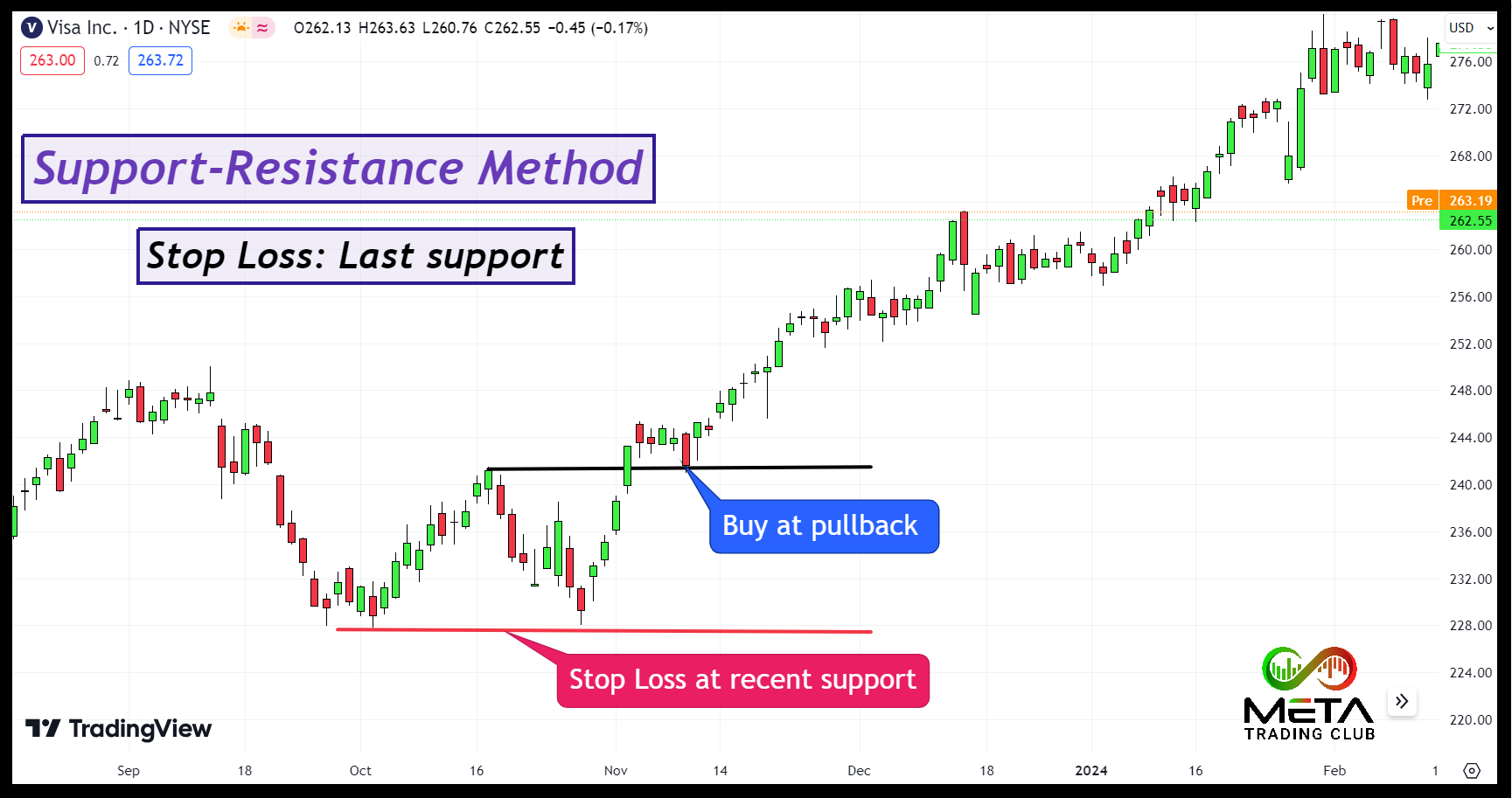
Support-Resistance Method
The support-resistance method for setting a stop loss by identifying the most recent support level of the stock and placing the stop price just below that level. This method relies on technical analysis to find a price level where the stock has historically had difficulty falling below. Here’s how you can apply it:
- Identify support and resistance levels: Support is a price level where the asset tends to find buying interest, preventing it from falling further. However, resistance is a price level where the asset tends to find selling interest, preventing it from rising further. You can identify them by using technical analysis.
- Determine your entry point: Decide where you will enter the trade based on the identified support or resistance levels.
- Set the stop loss: For Long Positions, place the stop loss just below the support level. This ensures that if the price falls below support, it indicates a potential trend reversal, and you exit the trade to minimize losses. Also, for Short Positions, place the stop loss just above the resistance level. This ensures that if the price rises above resistance, it indicates a potential trend reversal, and you exit the trade to minimize losses.
For example, if you buy Visa shares at $242, and the support level is at $228, you might set your stop price at $227. This way, if the price drops below $228, you exit the trade to avoid further losses.
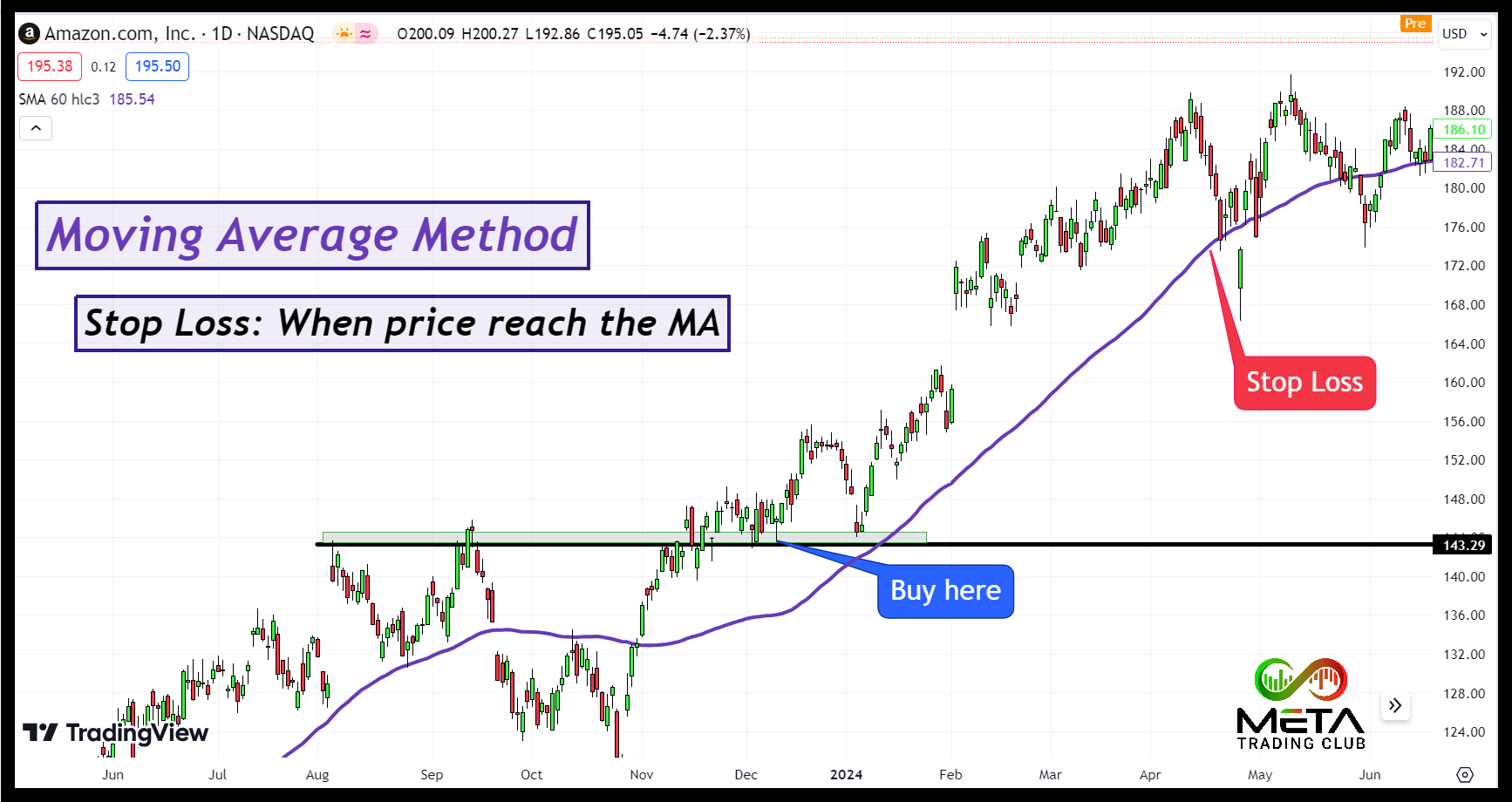
Moving Average Method
Using the moving average method to set stop loss orders is a popular strategy among traders. A Moving Average (MA) is a technical indicator that smooths out price data to identify trends over a specific period. Common types include the Simple Moving Average (SMA) and the Exponential Moving Average (EMA). Here’s a concise overview of how it works:
- Identify the moving average: Choose an appropriate moving average based on your trading style and timeframe. For instance, short-term traders might use a 20-day MA, while long-term traders might prefer a 200-day MA.
- Determine the trend: If the price is above the moving average, it indicates an uptrend; if below, a downtrend.
- Place the stop loss: For an uptrend, place the stop price just below the moving average. However, for a downtrend, place the stop price just above the moving average or the most recent swing high.
if you’re trading Amazon shares at $143 and the 60-day SMA is at $136, you might set your stop price just below $136. As the price goes up the SMA and your stop loss will trail. This helps protect your position if the price drops below the moving average, indicating a potential trend reversal. As you can see in this example your stop trailed to $173 (it’s not stop loss any more it’s a profit target).
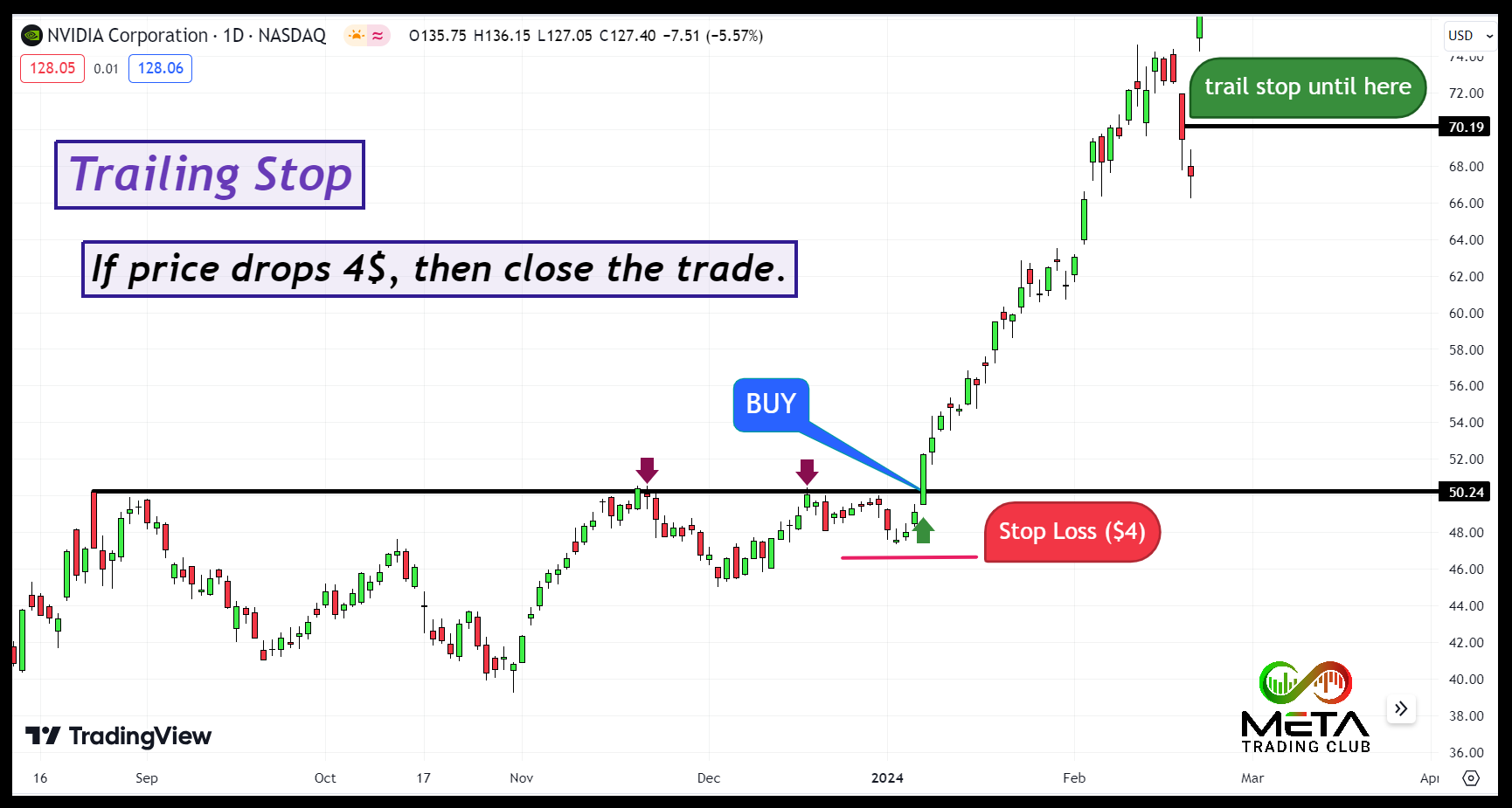
Trailing Stop
A trailing stop is a dynamic stop loss order that adjusts itself as the price of a security moves in your favor. Also, trailing stop is set at a specific percentage or dollar amount away from the current market price. As the price moves in your favor, the trailing stop moves with it, helping to lock in profits while limiting potential losses. Here’s a detailed overview of how it works:
- Initial setup: When you place a trailing stop, you specify the trailing amount (either as a percentage or a fixed dollar amount). For example, if you set a $4 trailing stop on a stock priced at $100, the stop-loss will initially be set at $96.
- Price movement: If the stock price rises to $110, the trailing stop will move up to $106 ($4 below the new high). However, if the stock price then falls to $108, the trailing stop remains at $106. If the price drops further to $106, the stop loss order is triggered, and the position is sold.
Imagine you bought Nvidia at $50 and set a trailing stop at $4. If the stock price rises to $75, the trailing stop moves up to $71. If the price then falls to $71, the stop-loss order is triggered, and the stock is sold, securing a $21 profit per share.
Notice that it’s crucial to set the trailing amount at an appropriate level. If you choose your trailing stop too tight, then the normal market fluctuations might trigger the stop. However, if you pick a too wide trailing stop, you might give up more profit than necessary. In addition, trailing stops are particularly useful in volatile markets where prices can swing significantly.
Advantages of Stop Loss Orders
Stop loss orders offer several advantages for traders. Here, we are going to explain some key benefits:
- Risk limitation: A stop loss order is designed to limit a trader’s loss on a security position that makes an unfavorable move. For example, if you set a stop loss order for 10% below the price at which you bought a stock, your loss will be limited to 10%. This risk management feature helps protect your capital.
- Emotion-free decision-making: Stop orders help insulate your decision-making from emotional influences. Also, traders sometimes become attached to stocks, hoping they’ll turn around. However, delaying a sale may only lead to greater losses. Having a predefined stop loss level ensures discipline and prevents emotional biases and ensures that you stick to your trading plan and avoid panic selling.
- Automation: Stop loss orders allow you to automate your trading strategy, ensuring that your positions are managed even when you are not actively monitoring the market. Once the stop price is triggered, the trade is automatically closed at the prevailing market price. This convenience is especially handy when you’re unable to watch your stocks consistently, such as during vacations or busy periods.
- Protection of profits: They can be used to lock in profits by setting a stop price above the purchase price, ensuring that gains are protected if the market reverses.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that your positions are protected by stop loss orders can provide peace of mind, allowing you to focus on other aspects of your trading strategy.
Note that while stop loss orders have advantages, they can also be triggered by short-term price fluctuations, potentially leading to unnecessary sales. It’s essential to set stop levels carefully based on your risk tolerance and trading strategy. If you want to build a disciplined trading strategy, participate in our 4-weeks incubator program.
Disadvantages of Stop Loss Orders
While stop loss orders offer advantages, they also come with some drawbacks. Let’s explore them:
- Market volatility: In highly volatile markets, the price of a security can fluctuate significantly in a short period. Also, this can trigger the stop order prematurely, resulting in an unintended sale.
- Gaps in trading: If a stock opens at a much lower price than its previous close (a gap down), the stop loss order will be executed at the next available price, which could be significantly lower than the stop price.
- No guarantee of execution price: Stop loss orders become market orders once triggered, meaning they will be executed at the next available price. Also, this price might be different from the stop price, especially in fast-moving markets.
- False sense of security: Relying solely on stop orders might give traders a false sense of security. It’s important to use them as part of a broader risk management strategy.
- Potential for frequent trading: In volatile markets, stop loss orders can lead to frequent buying and selling, which can increase transaction costs and reduce overall returns
Final Words
Stop loss orders serve as crucial risk management tools in the financial markets. By automatically closing a trade when its price reaches a predetermined level, they shield traders from further losses. Regular stop orders trigger at specific prices, while trailing stop orders dynamically adjust as stock prices move in your favor. Keep in mind that execution may not always occur at the exact stop price due to market fluctuations.
Using stop loss orders effectively can help protect your investments and manage risk. Choose stop price levels that align with your risk tolerance and trading strategy. Also, once you set your stop loss, avoid moving that unless your strategy requires it. Moreover, use stop loss orders alongside other risk management tools for a comprehensive approach and adjust your stop loss strategy based on market volatility and trends.
FAQs
- How does stop-loss work?
For example, if you buy shares of Nvidia at $120 per share, you might set a stop loss at $115. When the stock price falls below your specified stop price ($115), the stop loss order becomes active. The brokerage platform automatically sells your shares at the prevailing market price. - What is called stop-loss?
This is a type of order that traders use to limit their potential losses in the stock market. Also, it works by automatically selling a security when its price reaches a certain level, known as the stop price. - When should I use a stop-loss?
You should use a stop price to limit potential losses on a trade. During volatile market conditions or news events, a stop loss helps protect your position. Even for long-term investments, consider a stop loss to safeguard against unexpected declines. - What is the 1% rule for stop loss?
The 1% rule is a risk management guideline used by traders. You’re allowed to risk up to 1% of your trading account on any single trade. Adjust your position size so that when your stop-loss order is triggered, your total loss equals 1% of your account. - Do successful traders use stop losses?
Yes, successful traders do use stop losses as part of their risk management strategy. Because by setting a stop price, traders limit potential losses and secure profits.