In the unpredictable world of trading, risk management is the cornerstone of long-term success. Every trade carries intrinsic risks, and without a solid strategy to manage these risks, even the most promising opportunities can lead to significant losses. Effective risk management involves identifying potential threats, assessing their impact, and implementing measures to mitigate them. By mastering risk management techniques, you can protect your capital, minimize losses, and maximize your chances of achieving consistent profitability. Let’s explore the essential strategies that you should know to navigate the complexities of the market with confidence.
Table of Contents
What is Risk in Trading?
In trading, risk refers to the potential for financial loss or performance that exceeds expectations. This risk stems from various sources: market volatility, economic shifts, geopolitical events, and other unforeseen market dynamics. Understanding risk in trading is not just about acknowledging the possibility of losses. It’s also about quantifying these risks and comprehending their origins.
Managing risk is crucial for sustaining success in volatile markets where both gains and losses are significant.
Types of Trading Risks
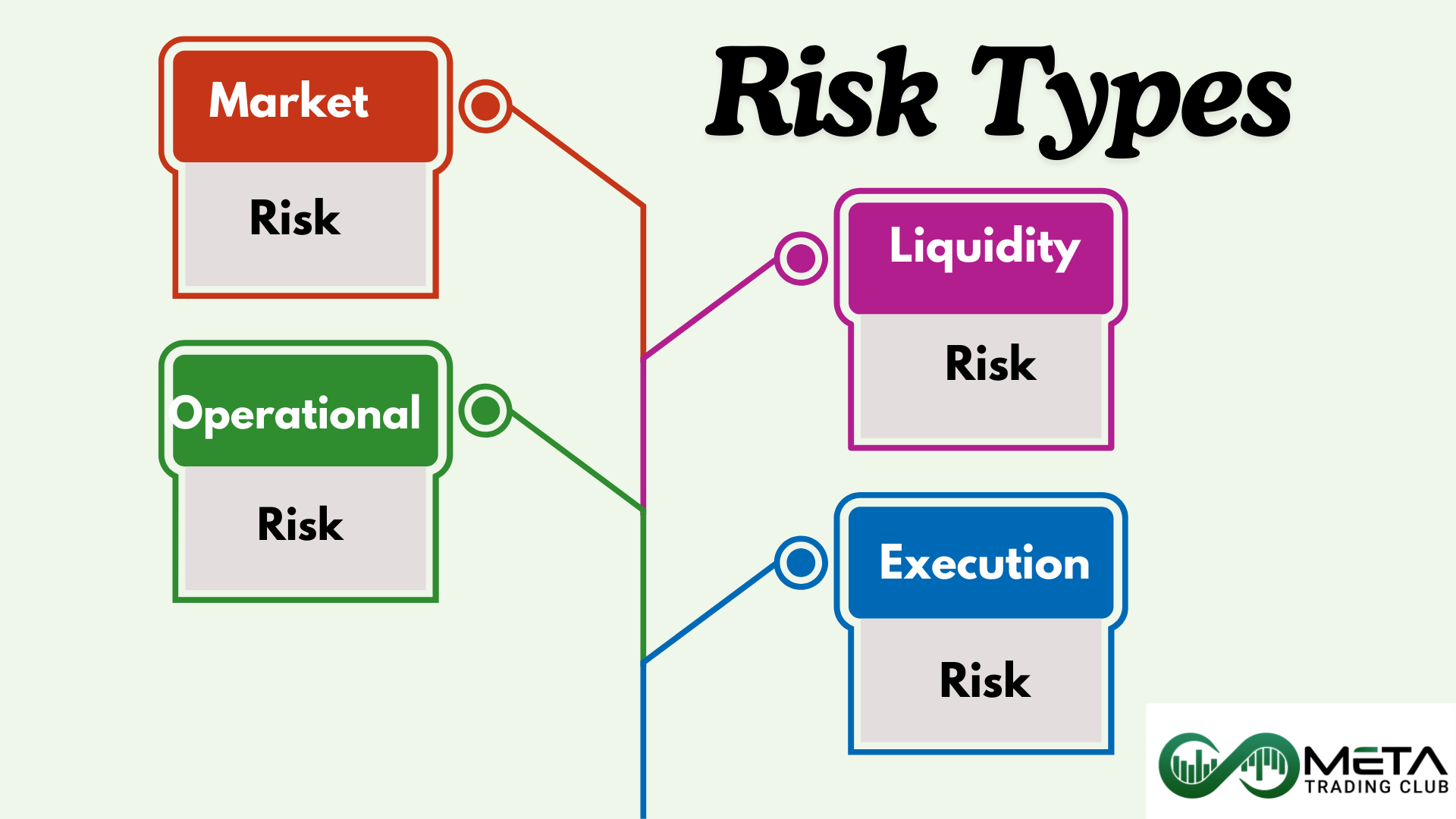
Traders encounter various types of risks when participating in financial markets. These risks are inherent in trading and being aware of them can help in formulating sound risk management strategies. Here are several common risks that you need to manage effectively.
1- Market Risk
Market risk refers to the possibility that a trader’s positions will suffer losses due to unfavorable movements in market prices. Also, market risk, also known as systematic risk, refers to the uncertainty associated with trading due to factors affecting the overall performance of financial markets.
Besides, market risk influences the entire market simultaneously and cannot be eliminated through diversification. Market risk is the most common type of risk traders face and involves various factors such as changes in interest rates, exchange rates, economic conditions, and geopolitical events.
Diversification helps mitigate specific risks (or unsystematic risk that is unique to a specific company or security and can be reduced through diversification), but market risk remains inherent.
2- Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk refers to the potential difficulty associated with inability to execute transactions at prevailing market prices due to insufficient market depth or disruptions.
This risk occurs when you can’t buy or sell an asset quickly enough to prevent a loss. Besides, illiquid markets or sudden price gaps can exacerbate this risk.
For example, imagine a sudden surge in demand for a stock, causing its price to spike. If you hold that stock but can’t sell it quickly due to low trading volume, you face market liquidity risk.
3- Operational Risk
This risk refers to the uncertainties and hazards related to a trader’s day-to-day activities, processes, and infrastructure. Operational risk heavily depends on human actions or decisions within a trading environment.
Also, mistakes, errors, or failures made by traders or other staff contribute to operational risk. Flaws in systems, processes, or technology (like technical issues, software errors) can lead to operational risk. So, you must ensure robust risk management procedures to mitigate this risk.
4- Execution Risks
Execution risk in trading refers to the possibility that the execution of buy or sell order will not occur at the desired price. This can happen due to slippage, which represents the difference between the expected price of a trade and the actual execution price. In other words, slippage occurs when market conditions cause the trade to be executed at a different price than anticipated. However, traders often use limit orders and stop-loss orders to manage execution risk and minimize slippage.
What is Risk Management?
Risk management is any strategy taken to minimize risk during a trade. For example, a hedging strategy aims to decrease the amount you would lose if your trade moves against you by opening additional positions that balance your exposure.
Risk management in trading involves identifying, assessing, and controlling potential losses in your trading account. It’s a crucial process for navigating volatile markets where both gains and losses can be significant. Also, traders use various tools and strategies to minimize risks while maximizing potential profits. These include setting stop-loss and take-profit points, diversifying portfolios, and using protective measures like options or hedging.
Principles of Risk Management in Trading
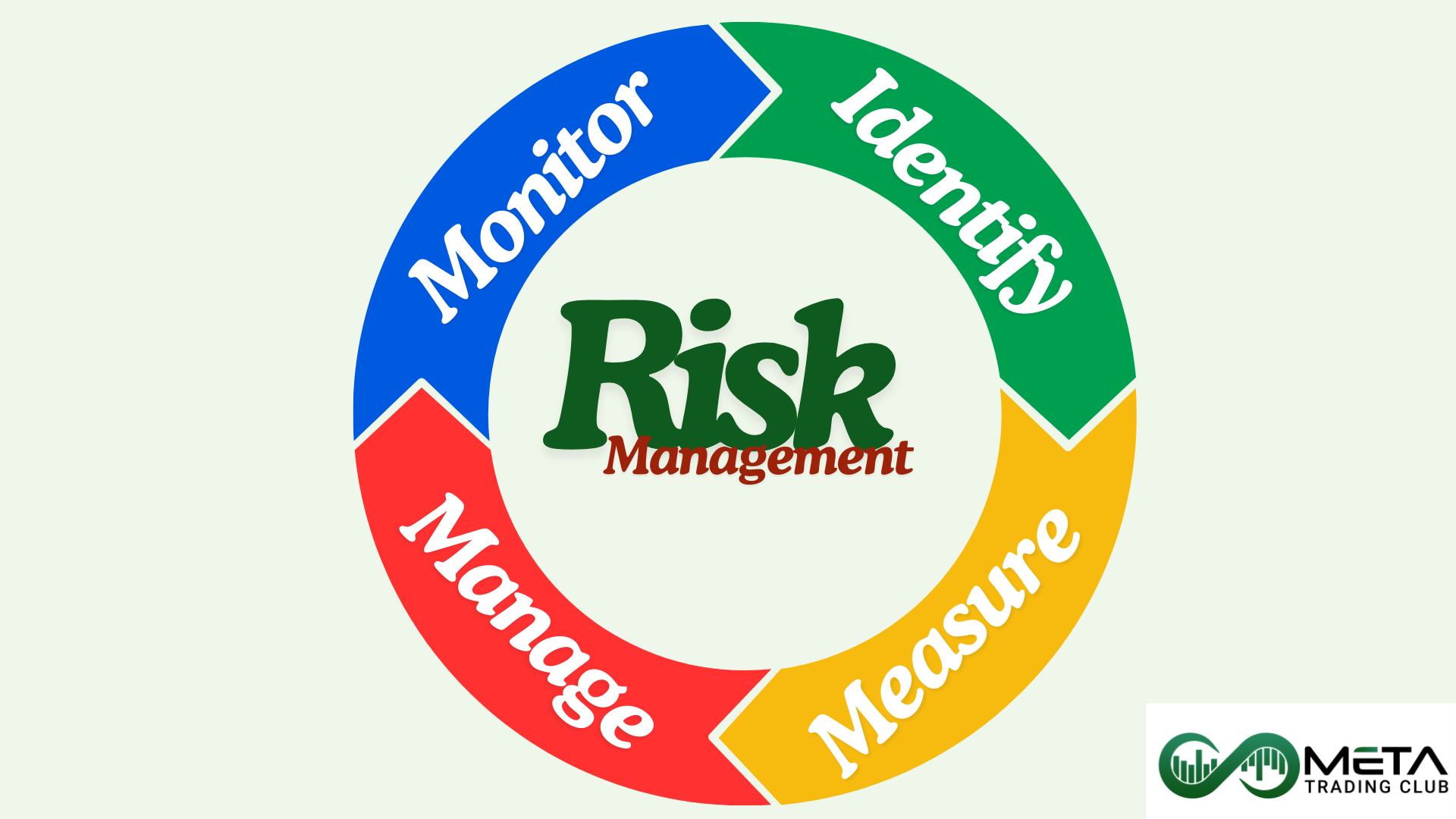
Effective risk management is crucial for success in trading. Understanding the key principles and implementing these principles can help you protect your accounts, minimize losses, and increase profitability. Let’s explore the key principles:
1- Identifying Risks
The first step in risk management is to understand the potential risks associated with each trade. These could include market risk, execution risk, and liquidity risk. You should identify specific risks related to the asset, industry, or market segment you’re trading. Besides, understanding the different types of risks enables you to make informed decisions and select appropriate strategies to minimize potential losses.
2- Measuring Risks
Once you have identified the risks, it is crucial to measure them and determine the potential impact on your trading account. So, quantify risk by assessing factors such as stop-loss levels, position size, and volatility. Calculate risk-reward ratios to evaluate potential gains against potential losses. Also, by quantifying the risks, you can set realistic targets and continually improve their risk management strategies.
3- Managing Risks
After identifying and measuring risks, you should implement risk management strategies to control potential losses. You Implement strategies to mitigate your risk (we’ll explain these strategies in the next section). Also, you can diversify your portfolio to reduce exposure to any single asset or market. Note that, establishing clear rules and guidelines for managing risk enables you to navigate volatile markets more effectively. If you want to learn how to manage your risks accurately, participate in our 4-weeks incubator program.
4- Monitoring Risks
Continuously monitor your trades and stay informed about market developments and news that could impact your positions. Also, by reviewing your trades regularly, you can identify areas for improvement and adapt to changing market conditions.
Keep track of your win/loss ratio, average win and loss size, and risk/reward ratio to ensure your risk management practices remain effective and continue to protect your trading account.
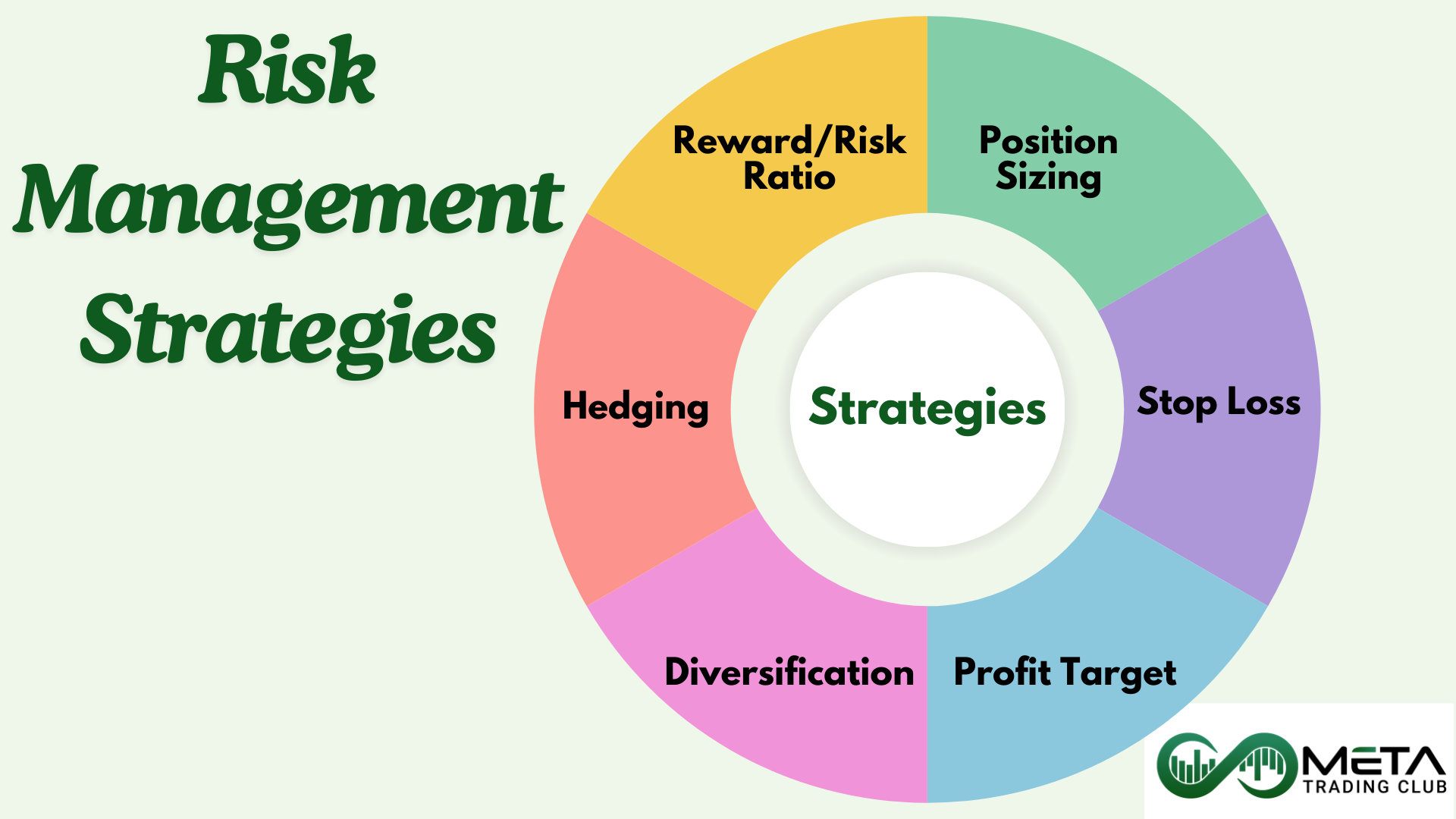
Risk Management Strategies
Employing risk management strategies is akin to a captain commanding the ship to sail safely through turbulent seas. Such techniques serve as navigational tools that steer the vessel through choppy waters toward secure moorage. Here are some common risk management techniques used in trading:
1- Position Sizing
This technique involves determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to a specific trade based on your risk tolerance and account size. It’s crucial to avoid risking too much on any one position. Smaller position sizes reduce the impact of losses and allow you to stay in the game even after a series of unsuccessful trades. In addition, you can explore position sizing strategies in the Position Sizing article.
For example, if you decide to risk 2% of your $10,000 trading account on a trade, you will risk $200. If your stop-loss is set at $20 per share, you would buy 10 shares ($200 / $20 per share) to maintain proper position sizing.
2- Stop Loss
A stop loss order is a predefined price level at which you’ll exit a trade to limit potential losses. Stop loss orders help prevent emotional decision-making during market volatility. Also, you can read the Stop Loss article in order to learn how to set a stop loss.
For example, if you buy a Tesla (TSLA) at $250 and set a stop-loss order at $240. If the Tesla price drops to $240, the order triggers and the stock will be sold automatically. This prevents further losses and limits your loss to $10 per share.
3- Profit Target
A profit target is a specific price level at which you plan to exit a trade to secure a profit. It is set based on your analysis and expectations of how far the price will move in your favor.
By setting a profit target, you can lock in gains and avoid the temptation to hold onto a position for too long, which might result in losing the profits if the market reverses. Also, if you are interested in learning strategies to set an appropriate profit target, read the Profit Target article.
Suppose you are short on a currency pair (expecting its price to fall), you might set a take profit order at the recent resistance level. If the price reaches that level, the order executes and secures your gains. This way, you ensure that you capture gains without getting greedy and risking a potential reversal.
4- Diversification
Diversification involves spreading your investments across different assets or markets (it’s an investment strategy). By diversifying, you reduce the impact of a single asset’s poor performance on your overall portfolio.
For instance, instead of investing all your capital in one stock, consider allocating some funds to bonds, commodities, or other assets. Besides, by spreading your investments across different assets or markets, reduce the impact of a single loss on your overall portfolio.
5- Reward-Risk Ratio
The reward-risk ratio (also known as the risk-reward ratio) is a measure used to compare the potential profit of a trade to its potential loss. It helps you evaluate whether a trade is worth taking based on the expected return relative to the risk involved. Also, you can learn more about this ratio in the reward/risk ratio article.
If you enter a trade with a potential profit of $200 and a potential loss of $100, the reward-risk ratio would be: $200/$100 = 2:1. This means that for every dollar you risk, you expect to make two dollars in profit.
Calculating this ratio helps you assess whether a trade is worth taking. However, raders often set a minimum reward-risk ratio for their trades, such as 2:1 or 3:1, to ensure that the potential rewards justify the risks.
6- Hedging
Hedging is a risk management strategy used to offset potential losses by taking an opposite position in a related asset. The main goal of hedging is to reduce the risk of adverse price movements in an asset. Also, it acts like insurance, protecting your trades from significant losses.
You can hedge by making offsetting trades in securities with negative correlations. For example, if you own a stock, you might buy a put option on the same stock to protect against a price drop.
Hedging is a valuable tool for managing risk, but it’s important to understand that it can also limit potential profits. It’s about finding a balance between risk and reward.
Benefits of Risk Management in Trading
Risk management is crucial for sustainability in trading. It ensures that you can withstand losses without significantly impacting their capital. Besides, risk management offers several benefits in trading like:
- Capital preservation: By managing risk, you can protect capital from significant losses. Also, preserving capital ensures your durability in the markets.
- Reduced emotional stress: Risk management strategies help you avoid emotional decision-making. Moreover, fear and anxiety decrease when you know your risk exposure is controlled.
- Consistent trading approach: Risk management enforces discipline and consistency. Also, by sticking to your predefined rules, you can reduce impulsive actions.
- Improved decision-making: Traders evaluate potential gains against potential losses. So, clear risk assessments lead to better trade decisions.
- Long-Term viability: Effective risk management ensures you can participate in the markets over the long term. It prevents account wipeouts due to a few bad trades.
It’s important to know that risk management isn’t just about avoiding losses; it’s about maximizing gains while safeguarding your trading capital.
Psychological Aspect of Risk Management
The psychology of risk involves understanding the mental processes underlying our responses to risky situations, recognizing the impact of risks, and developing frameworks for sound decision-making in the face of uncertainty. The psychological aspects of risk management in trading are crucial for maintaining discipline and making rational decisions. Here we discuss some aspects:
- Emotional regulation: Emotions like fear, greed, and overconfidence can significantly impact trading decisions. Fear can lead to premature selling, while greed might cause holding onto losing positions for too long.
- Cognitive biases: Traders often fall prey to biases such as confirmation bias (favoring information that confirms their beliefs) and loss aversion (preferring to avoid losses rather than acquiring equivalent gains). These biases can lead to suboptimal trading decisions.
- Discipline and patience: Successful traders maintain discipline by sticking to their trading plans and not letting emotions dictate their actions. Also, patience is essential, it helps traders wait for the right opportunities rather than making impulsive decisions.
- Stress management: Trading can be stressful, and managing this stress is vital for maintaining a clear mind. Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and regular breaks can help traders stay focused and calm.
- Self-awareness: Understanding one’s own psychological tendencies and how they affect trading decisions is crucial. Besides, keeping a trading journal can help traders reflect on their decisions and improve their strategies.
- Risk tolerance: Each trader has a different level of risk tolerance, which should be acknowledged and respected. Understanding and setting personal risk limits can prevent emotional trading and significant losses.
By addressing these psychological factors, you can improve your decision-making and risk management processes. Also, enhance your overall trading performance.
Final Words
Risk management is not just a safety net but a vital component of successful trading. By understanding and implementing effective risk management strategies, traders can navigate the complexities of the market with greater confidence and resilience. Remember, the goal is not to eliminate risk entirely (which is an impossible task) but to manage it in a way that protects your capital and maximizes your potential for profit. As you continue your trading, let risk management be your guiding principle, ensuring that you are well-prepared to face any market conditions that come your way.
FAQs
In trading, risk management is the process of identifying, analyzing, and taking steps to minimize potential losses and protect your capital. It involves setting limits on how much you can lose on a single trade and using strategies like stop-loss orders to control risks.
1. Identifying potential risks that could affect the organization or project.
2. Measuring the identified risks to understand their potential impact and likelihood.
3. Implementing measures to mitigate or manage the identified risks.
4. Monitoring your trade and stay informed about market news that could impact your positions.
The main purpose of risk management in trading is to minimize potential losses and protect your capital. This involves making informed decisions to balance potential risks and rewards, ensuring long-term profitability and sustainability in the market.
Risk management in forex trading involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential losses associated with currency trading. It includes strategies and techniques to protect trading capital from adverse market movements.
The 1% rule in trading suggests that a trader should not risk more than 1% of their total trading capital on a single trade. This means if you have $10,000 in your trading account, you should not risk more than $100 on any one trade. This rule helps to limit potential losses and preserve capital.
The common risk management techniques in trading are stop loss, profit target, diversification, position sizing, reward to risk ratio and hedging. Implementing these techniques can help traders manage risks effectively and improve their chances of long-term success.