Understanding the reward/risk ratio is crucial for anyone looking to maximize their trading returns and manage risk effectively. The reward/risk ratio is a fundamental concept in trading and investing that helps traders evaluate the potential profit against the potential loss of a trade. By aiming for a higher reward compared to the risk taken, traders can make more informed decisions and improve their chances of achieving consistent profitability. In this guide, we will explore the importance of the reward/risk ratio, how to calculate it, and strategies to implement it successfully in your trading approach.
Table of Contents
What is Reward/Risk Ratio?
The reward/risk ratio is a measure used in trading to compare the potential profit of a trade to its potential loss. It helps traders assess whether the potential reward justifies the risk taken.
- Reward is the potential profit you expect to make from a trade.
- Risk is the potential loss you might incur if the trade doesn’t go as planned.
Also, the reward/risk (R:R) ratio is a metric of how much you stand to profit for every dollar you risk on a trade. Essentially, this ratio quantifies the expected return on a trade in comparison to the level of risk undertaken.
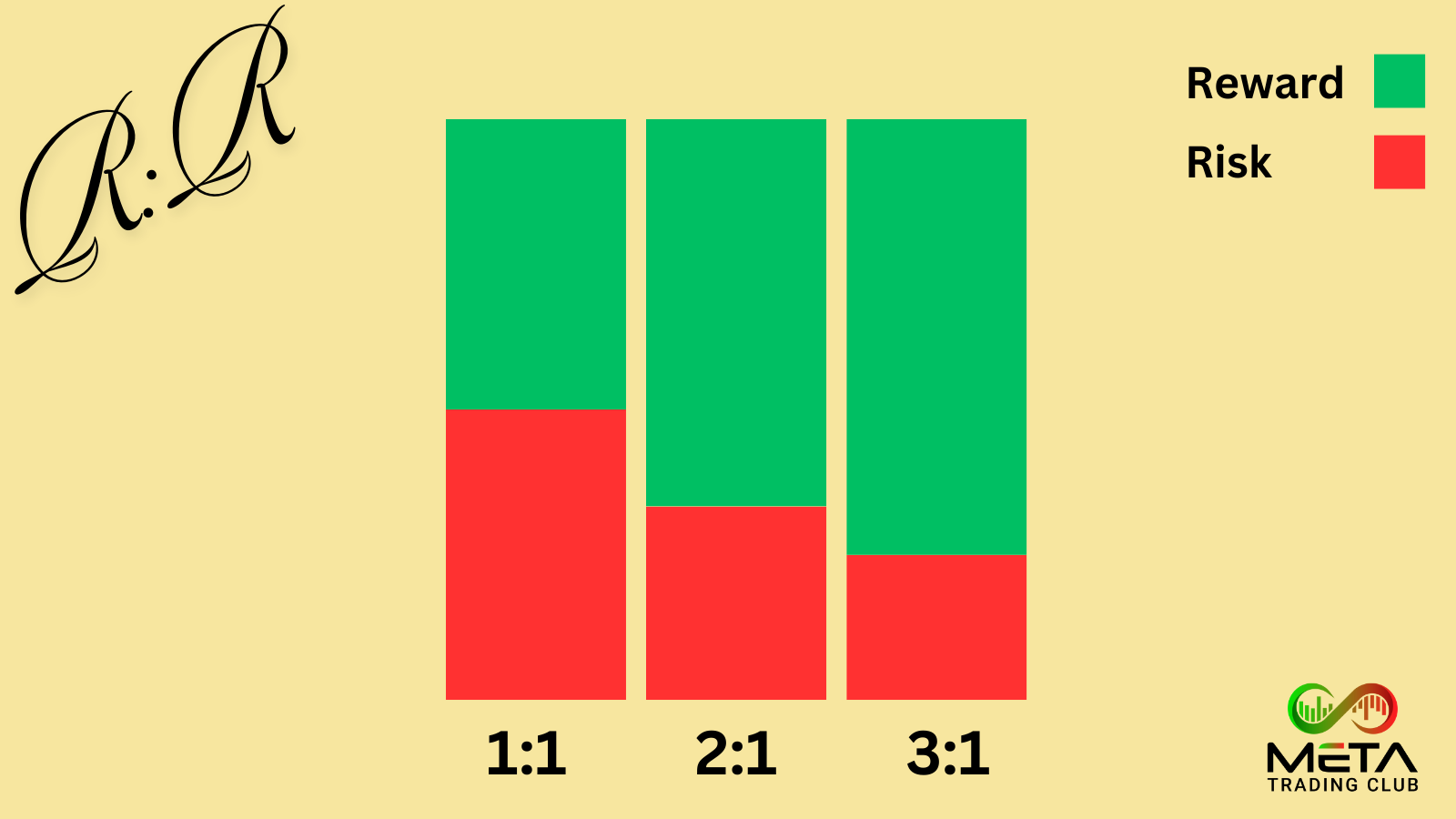
Using reward/risk ratios requires you to know what a good risk/reward ratio is. A reward/risk ratio of 1:1 means that the potential profit of a trade is equal to the potential loss. For example, if you risk $100, you expect to make $100 in profit. Although, many traders aim for higher ratios, like 2:1 or 3:1, to ensure that the potential rewards outweigh the risks.
How to Calculate Reward/Risk Ratio?
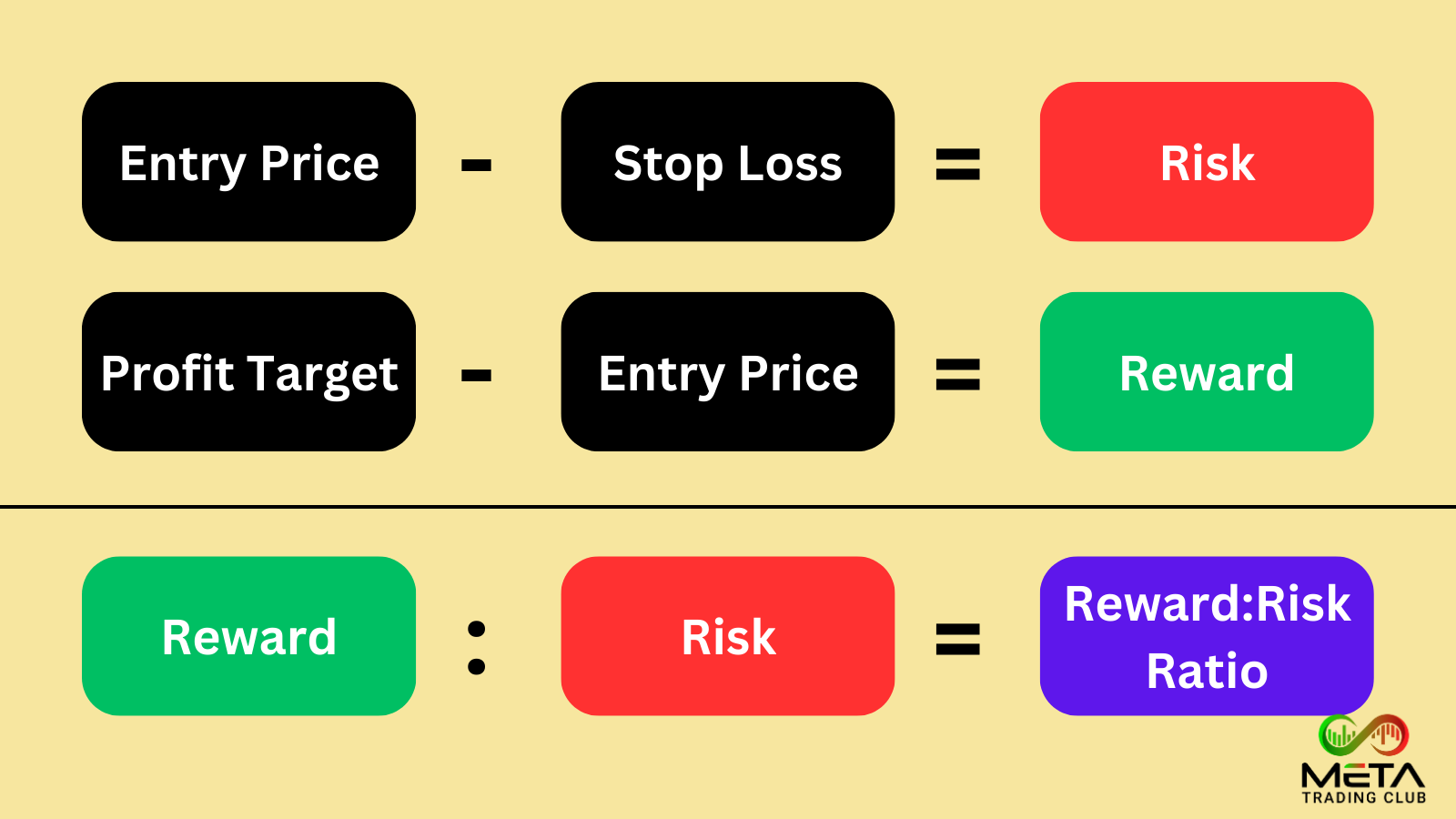
The reward/risk ratio helps in making informed decisions by comparing the expected returns to the potential losses. Calculating reward/risk ratio for a trade requires that you know your entry price, your profit target, and your stop loss.
Potential Reward
This is the amount you expect to gain if the trade is successful. Your reward for a long position is equal to the difference between your profit target and entry price (the amount you’ll gain if your trade goes according to plan).
For example, if you buy a stock at $50 and expect it to rise to $80, your potential reward is $30.
Potential Risk
This is the amount you could lose if the trade does not perform as expected. Your risk for a long position is equal to the difference between your entry and stop loss (the amount you’ll lose if your trade stops out).
Using the same example, if you buy the stock at $50 and set a stop-loss order at $40, your potential risk is $10.
The Ratio
The ratio = The Potential Reward / The Potential Risk
In this example, the ratio is 30/10= 3:1. This means for every dollar you risk, you expect to earn three dollars.
Example
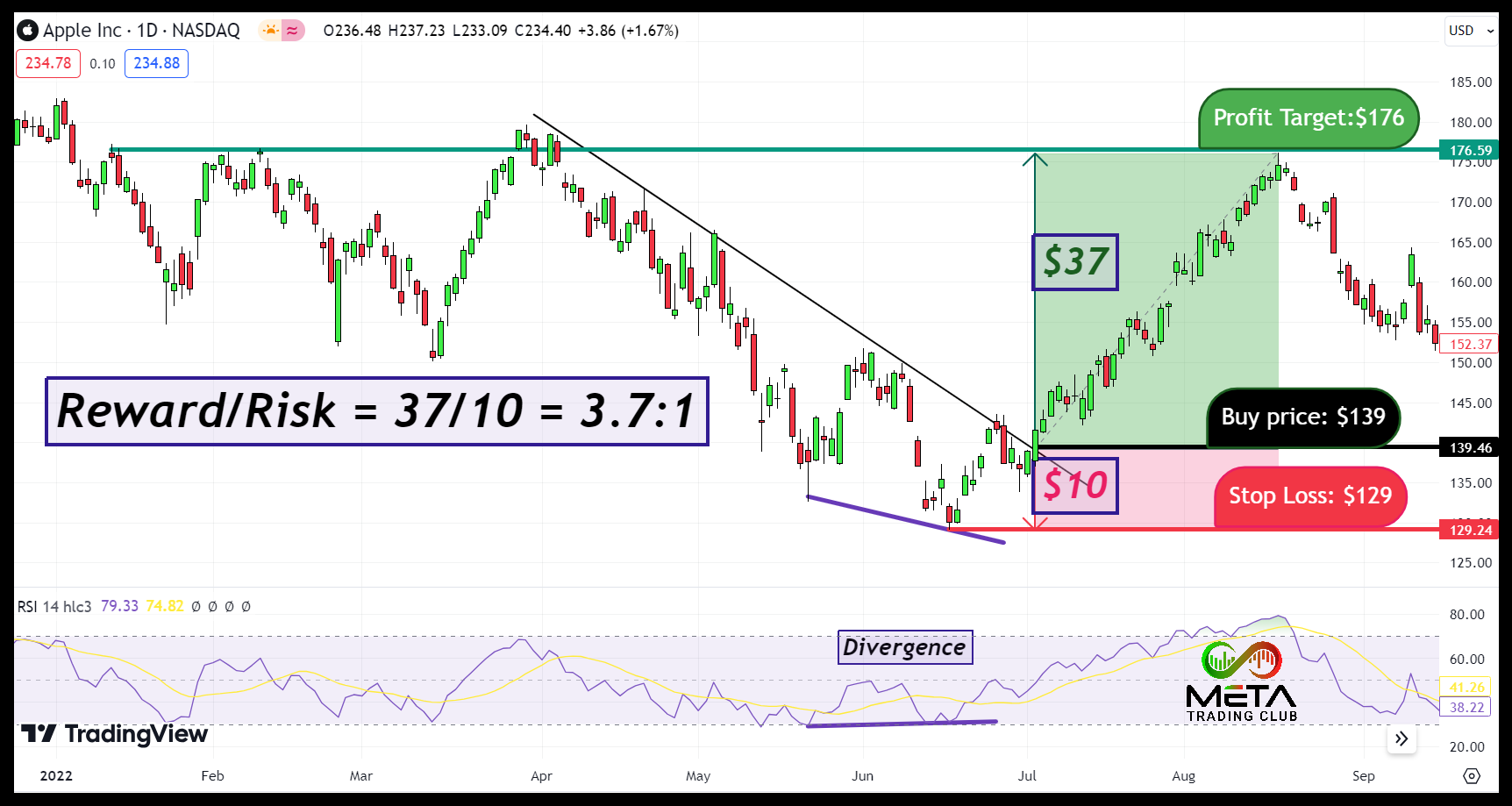
Consider a practical example, suppose you want to buy Apple stock. After your analysis, you determine that AAPL has the potential to increase in price after breaking the down-trend line from its current level of $139 to $176, but it could also decrease to $129. Here’s how you would calculate the reward/risk ratio:
- Potential Profit (Reward): If the price goes up to $176, your profit would be $176 – $139 = $37 per share.
- Potential Loss (Risk): If the price drops to $129, your loss would be $139 – $129 = $10 per share.
- Reward/Risk Ratio: The ratio is then calculated as $37 (Reward) / $10 (Risk) = 3.7
This means that for every dollar you risk, you expect to make 3.7dollars in return. This is a reward/risk ratio of 3.7:1.
Furthermore, you might decide that you’re only willing to enter trades with a reward/risk ratio of 3:1 or higher. This would mean that this trade meets your criteria. However, if you only accepted trades with a reward/risk ratio of 4:1 or higher, you would pass on this trade.
Remember, the reward/risk ratio is just one tool in your trading toolbox. It’s important to consider other factors like the overall trend of the market, the financial health of the company you’re trading, and your personal risk tolerance. Always make sure to do thorough research before making any trading decisions. If you want to boost your trading skills, participate in our 4-weeks incubator program.
The Optimal Reward/Risk Ratio
The optimal reward/risk ratio can vary depending on the trading strategy and individual risk tolerance. Also, volatile markets might require a higher ratio to compensate for increased risk. However, conservative traders might prefer a higher ratio, while aggressive traders might be comfortable with a lower ratio.
Steps to find the optimal reward/risk ratio
Finding the optimal reward/risk ratio involves several steps and considerations. There is steps to follow:
- Define your trading goals: Determine what you aim to achieve with your trade. Are you looking for long-term growth, short-term gains, or a mix of both?
- Assess your risk tolerance: Understand how much risk you are willing to take. This can depend on factors like your financial situation, trading horizon, and personal comfort with risk.
- Conduct market research: Analyze the market conditions and the specific assets you are interested in. Look at historical data, trends, and potential future performance.
- Set clear entry and exit points: Define your entry point (when you will buy) and exit point (when you will sell) for each trade. This helps in calculating potential rewards and risks.
- Calculate potential reward and risk: Estimate the potential profit if the trade goes as planned and the potential loss if the trade does not go as planned.
- Use tools and software: Utilize trading platforms and tools that can help you calculate and visualize the reward/risk ratio. Some platforms offer tools for this purpose (like tradingview).
- Adjust based on experience: Continuously monitor and adjust your reward/risk ratio based on your trading or investment experience. Learn from both successful and unsuccessful trades.
However, a commonly recommended ratio is 3:1. This means that for every unit of risk taken, the potential reward should be three times greater.
This ratio helps ensure that even if some trades are unsuccessful, the overall gains can still outweigh the losses. For example, if you risk $100, you should aim for a potential reward of $300.
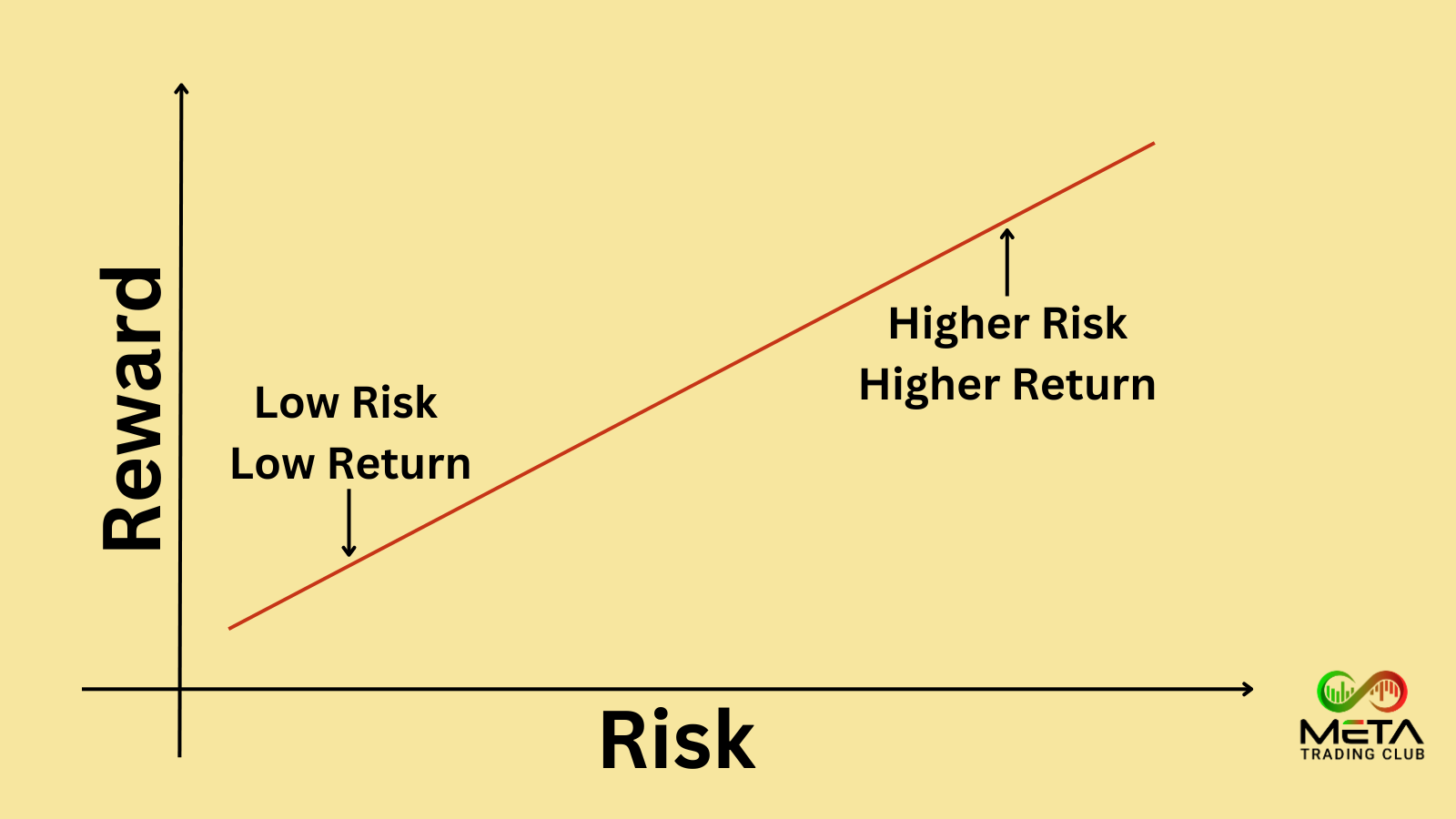
High Reward/Risk Ratio
A high reward/risk ratio is often desirable. Also, it’s also important to consider the probability of achieving the potential profit and the probability of incurring the potential loss. A higher ratio means that the potential reward is significantly greater than the risk, which can lead to substantial profits if the trade is successful. Also, by aiming for a higher reward relative to the risk, you can ensure that even a few successful trades can cover the losses from unsuccessful ones. In addition, it promotes careful selection of trade, focusing on those with the best potential returns.
On the other hand, trades with a high reward/risk ratio often have a lower probability of success, as higher rewards typically come with higher uncertainty. Traders might overestimate the potential rewards and underestimate the risks, leading to unrealistic expectations and potential losses. Also, high reward/risk trades can be more volatile, which might not suit all traders, especially those with lower risk tolerance.
The key is to find a balance that aligns with your trading goals and risk tolerance. A high reward/risk ratio can be beneficial if managed properly, but it requires careful planning and realistic expectations. It’s important to continuously monitor and adjust your strategy based on market conditions and personal experience.
Importance of Reward/Risk Ratio
The Reward/Risk Ratio is an important concept in trading, and it serves several key purposes:
- Risk Management: It helps traders manage their risk by giving them a sense of the potential profit compared to the potential loss of trade. A higher ratio means that the potential reward is greater than the potential risk, which might be more appealing to traders.
- Trading decision: If the potential loss is too great compared to the potential gain, a trader might choose to pass on the opportunity.
- Performance measurement: It can be used to measure the performance of a trading strategy over time. A strategy with a consistently high reward/risk ratio may be more successful than one with a lower ratio.
- Setting stop loss and profit target levels: It can help in setting the stop loss and take profit levels. For instance, if a trader is willing to take a reward/risk ratio of 3:1, he could set his stop loss at a level where they could lose $1 and their take profit at a level where they could gain $3.
Reward/risk ratio is a valuable tool, but it should not be the only factor considered when making trading decisions. Also, other factors such as market conditions, trading horizon, and individual financial circumstances should also be taken into account.
Limitations of Using Reward/Risk Ratio
While reward/risk can be a useful tool for assessing trading opportunities, it does have some limitations:
- Doesn’t account probability: The reward/risk ratio doesn’t take into account the probability of the outcomes. However, a trade might have a high potential reward and a low potential risk, but if the likelihood of achieving that reward is extremely low, the ratio alone might be misleading.
- Based on estimates: The ratio is based on estimated values for potential reward and risk, which may not be accurate. Also, market conditions, economic factors, and unforeseen circumstances can all impact the actual reward and risk.
- Doesn’t consider time: The reward/risk ratio doesn’t factor in the time it might take to realize the potential reward. Moreover, a trade with a high reward/risk ratio might not be as attractive if it takes a long time to see a return.
- Ignores other risks: The ratio typically only considers financial risk and reward, ignoring other types of risk such as operational, strategic, or reputational risks that could impact a trade.
Note that reward/risk ratio can be a helpful tool, but it’s important to consider a range of factors and not rely on it exclusively when making trading decisions.
Final Words
The reward/risk ratio is an essential tool for traders aiming to optimize their trading strategies. By understanding and applying this ratio, you can make more informed decisions, manage risks effectively, and enhance your potential for consistent profitability. Also, incorporating reward/risk ratio into your trading plan can significantly improve your trading outcomes. Remember, the key to have successful trades lies in balancing potential rewards with acceptable risks.
Moreover, mastering the reward/risk ratio requires continuous learning and practice. So, stay disciplined, keep refining your strategies, and always be mindful of the risks involved. In addition, with dedication and a solid understanding of the reward/risk ratio, you can navigate the complexities of the financial markets with greater confidence and success.
FAQs
The risk-reward ratio measures the potential profit compared to the potential loss of a trade. For example, a 1:2 ratio means you expect to earn $2 for every $1 risked.
A 1.5 risk-reward ratio means that for every dollar you risk, you expect to make one and a half dollars in profit.
Yes, a 2:1 reward-risk ratio is considered good. It means you expect to earn twice the amount you risk, which can be a good strategy for achieving consistent profitability.
The 2 percent rule in trading suggests that you should never risk more than 2% of your total account equity on a single trade. This helps manage risk and prevent significant losses.
A good risk-reward ratio is typically 1:2 or higher. This means you aim to earn at least two times the amount you risk on a trade. This ratio helps ensure that the potential rewards justify the risks taken.