Understanding how to calculate your position size is the first step toward making proper trading decisions. Also, accurate position sizing is vital for effective risk management, particularly if you’re just beginning your trading journey. Remember, position sizing is a fundamental aspect of successful trading. It’s not just about how much you can make; it’s about how much you can afford to lose.
Table of Contents
What is Position Sizing?
Position sizing refers to the number of units traded in a particular security by a trader. It involves determining the appropriate trade size based on factors such as entry price, stop-loss level, available capital, and the percentage of your account you’re willing to risk. By using position sizing, traders can control risk and maximize returns.
Proper position sizing involves finding the right balance between allocating a sufficient portion of your trading capital to enhance potential profits while minimizing the risk of significant losses. By implementing effective position sizing strategies, traders can protect their capital, enhance their trading performance, and maintain consistency in their overall trading approach.
Also, by adhering to proper position sizing, the trader ensures that they are risking a predetermined amount of their trading capital on each trade. This approach helps them maintain consistency in their risk management and prevents them from exposing too much capital to a single trade.
Why Position Sizing is Important?
Position sizing is critical for traders and the main benefit of that is risk management. Below are five main benefits of using position sizing.
- Risk management: Proper position sizing helps manage risk effectively. By determining the right position size, traders limit potential losses on individual trades. This prevents a single bad trade from significantly impacting their overall account.
- Consistency: Consistent position size ensures uniform risk across different trades. Whether trading stocks, options, or futures, maintaining a consistent approach helps traders stay disciplined and avoid emotional decision-making.
- Maximizing returns: Position sizing allows traders to allocate capital efficiently. In addition, by sizing positions appropriately, they can maximize returns while still adhering to risk limits.
- Psychological impact: Overcommitting to a trade due to improper position sizing can lead to stress, anxiety, and poor decision-making. However, proper sizing promotes emotional stability.
- Maintains trading discipline: Using a rules-based sizing approach promotes discipline by removing emotion-driven decisions. Also, traders are less likely to overtrade.
Best Position Sizing Strategies
There is no optimal model for choosing the size of trade. Just like with trading strategies, it all comes down to testing and exploring which method suits you best as a trader.
It is important not to abruptly change or mix different position sizing techniques, but rather to have a proper plan in place and ensure consistency. A demo trading account is the perfect solution if you need more time to explore which method is the best fit for your trading style. Here’s some of best position size strategies:
1. Fixed Dollar Value Risk
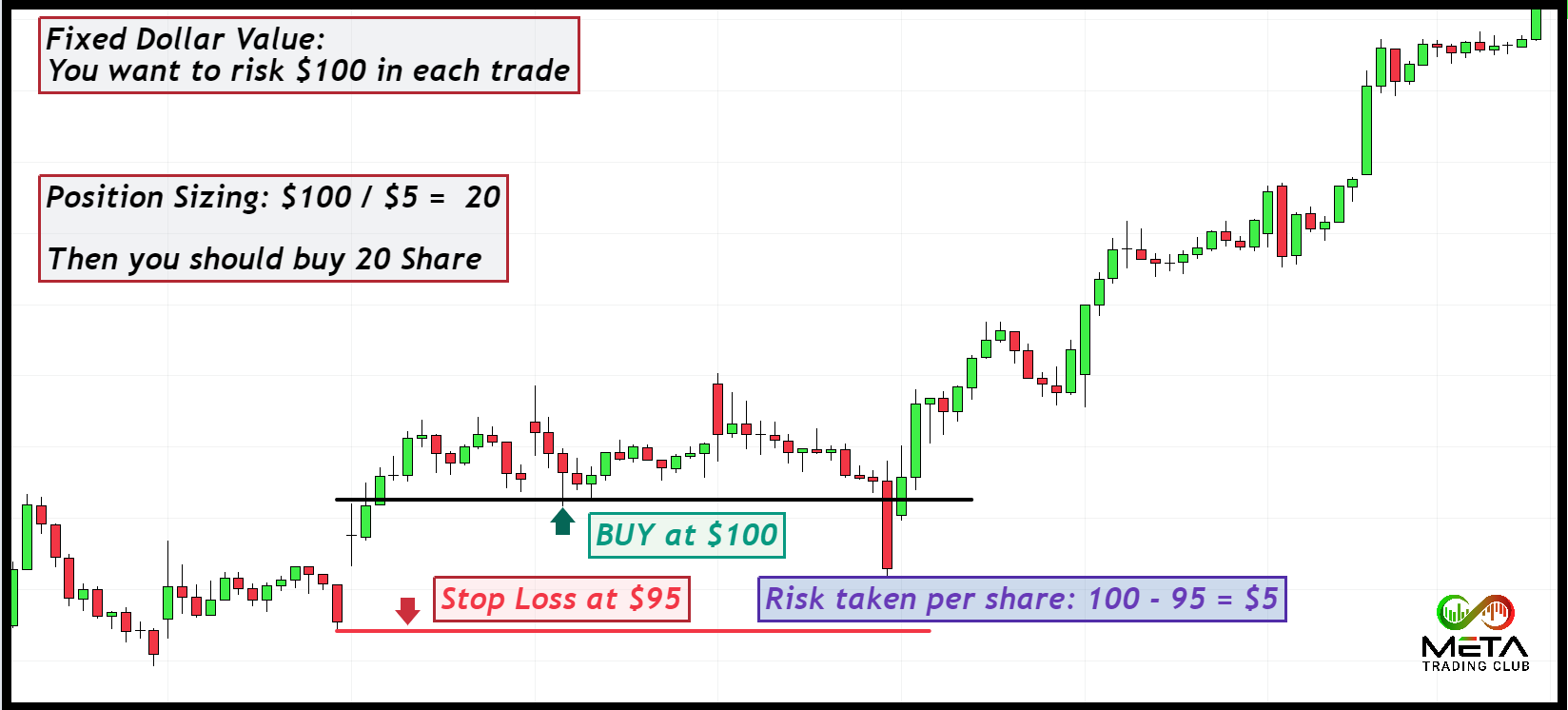
Fixed dollar value is a position-sizing strategy where the trader chooses the position size according to the Risk, they are willing to take. This automatically limits the risk you’re taking per trade. It will also help preserve your capital in case the first few trades you take turn out to be losses. The dollar amount determines the Risk here. Let us look at an example to understand this.
For example, you’re comfortable risking $100 per trade.
For calculating your position size based on this fixed risk. Consider the difference between your entry price and stop loss level. Divide your risk amount by this difference to find the appropriate position size.
For instance: If your stop loss is $5 below your entry price, your risk per share is $5.
With a $100 risk, your position size would be $100 / $5 = 20 shares.
2. Fixed Percentage Risk
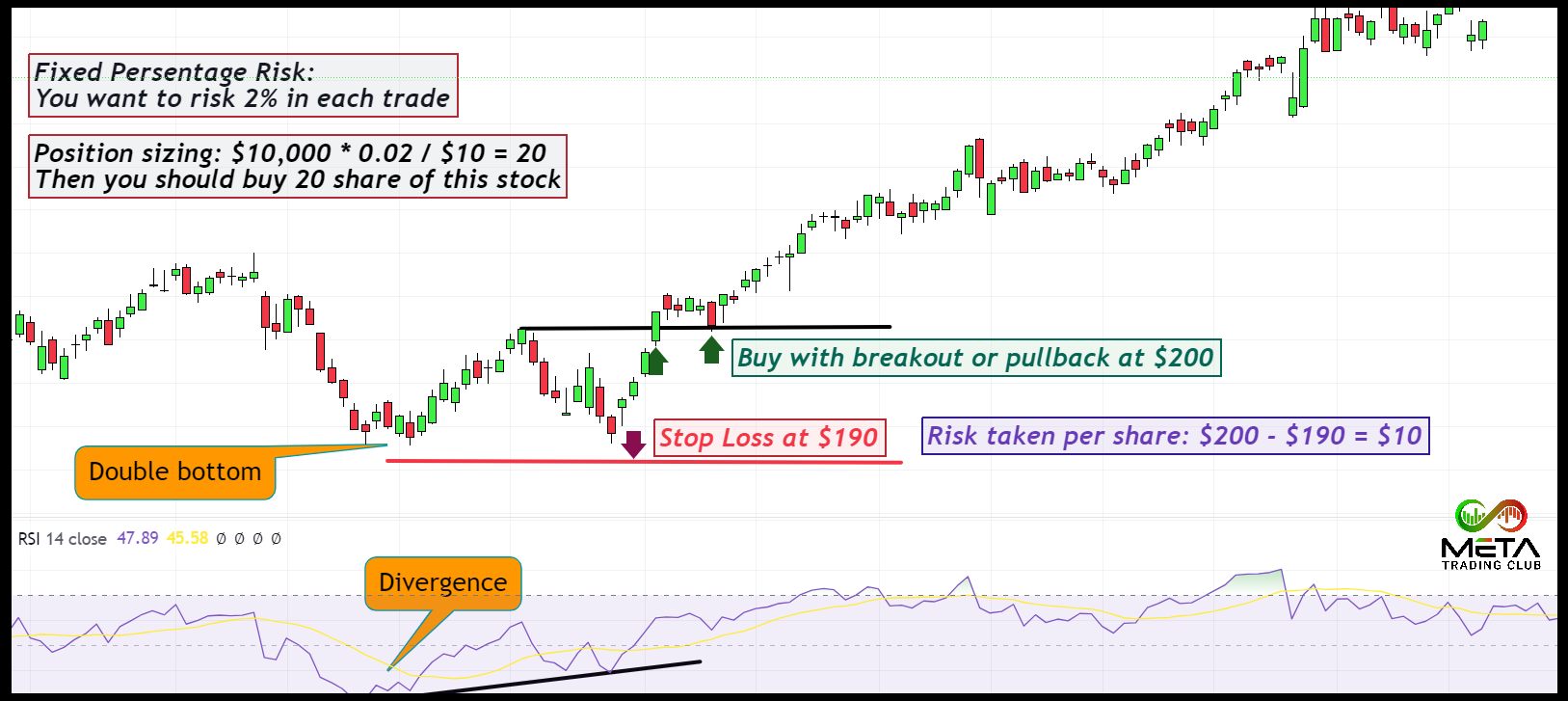
Determine the percentage of your trading capital that you’re willing to risk on each trade. A common rule of thumb is to risk no more than 1-2% of your capital per trade. When it comes to position sizing in trading, the fixed percentage risk per trade is a widely used strategy.
For example, you have $10,000 in your trading account, and you decide to risk 2% per trade. This means you’re willing to lose up to $200 on each trade.
If your stop loss is $10 below your entry price, your risk per share is $10.
With a 2% risk, your position size would be $10,000 * 2% / $10 = 20 shares.
Keep in mind that this percentage isn’t fixed in absolute terms. As the value of your trading capital changes, so does the amount you risk per trade.
For instance: If your capital increases to $15,000, your 2% risk moves from $200 to $300 risk per trade.
Conversely, if your capital decreases to $5,000, you still risk just 2% but it will be a smaller dollar amount $100. Hence it is an anti-martingale strategy.
However, choose a risk level that aligns with your risk tolerance and financial goals. Conservative traders may opt for a lower percentage (like 1%), while more aggressive traders might choose higher levels (up to 3-4%).
The great thing about this strategy is it gets you to focus on the percent risk instead of a dollar value. Note that the big risks you take in every trade can easily eat up your trading capital.
3. Volatility-Based
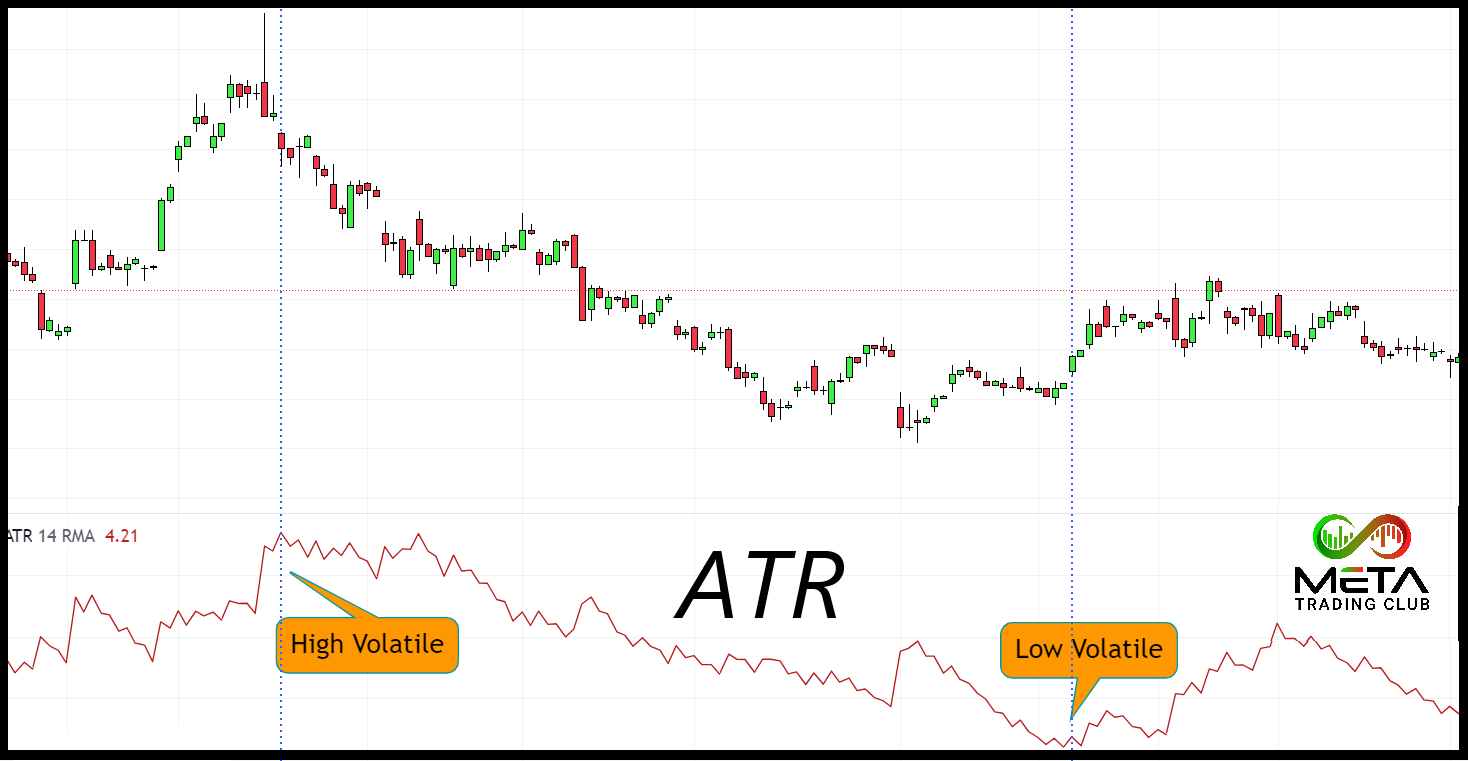
The volatility-based strategy is a method that adjusts the size of a trading position based on the market’s volatility. It acknowledges that not all trading instruments are created equal (some are more volatile than others). Therefore, it aims to standardize the level of risk across various trades and securities.
The core idea behind the volatility-based strategy is trade less when the market is more volatile and trade more when the market is less volatile. This is based on the assumption that when markets are volatile, the price swings are larger, and therefore, the risk is higher.
In this approach, a trader might use a volatility indicator like Average True Range (ATR) or standard deviation to quantify the market’s volatility. Once the volatility is calculated, it’s used to adjust the position size.
For instance, if stock is highly volatile, the trader might decide to reduce the number of units they’re buying to maintain their risk at a manageable level. And vice-versa.
Also, by adjusting the position size based on market volatility, traders can potentially reduce their exposure during volatile market periods and increase it when the markets are less volatile.
4. Contract Size Value
Contract Size is a position-sizing technique where traders always trade a fixed number of shares or contracts per trade. The contract size is predetermined based on the account size and risk tolerance. Many index and commodity traders use this strategy to limit their risks. The contract size value is an effective way of controlling your risk while getting exposure to a fast-moving market.
In this strategy, contract numbers remain the same for all trades and don’t change based on the trader’s capital, the market’s volatility, or other factors.
For example, if a trader decides to buy 2 contracts of a specific future contract, they will buy two contracts each time they make a trade, regardless of the contract’s price or the trade’s total value.
However, the contract size strategy doesn’t factor in the risk associated with each trade. Two contracts in a highly volatile market could represent a significantly larger potential loss than two contracts in a less volatile market. Also, this approach doesn’t adjust the size of the position relative to the size of the trader’s account, which can lead to disproportionate losses if a trade goes wrong.
In addition, the contract size strategy can be useful in certain circumstances, it’s usually combined with other strategies or risk management techniques to ensure the trader is not exposed to excessive risk. However, traders use stop-loss orders to limit their potential losses on each trade or adjust the size of their position based on the volatility of the market.
How to Reduce Risk Using Position Sizing Strategies?
Position sizing involves determining the appropriate amount of risk you are willing to take on each trade based on your account size, risk tolerance, and the specific characteristics of the trade. To implement position sizing safely, you need to consider the following factors:
- Account size: Assess your total account size and decide how much of it you are comfortable risking on a single trade. It is generally recommended to risk only a small percentage of your account, such as 1-2%, to safeguard against substantial losses.
- Stop loss: Determine the placement of your stop loss order, which is a predetermined level at which you will exit the trade if it moves against you. A well-placed stop loss can limit your potential losses and help you maintain a safe risk profile.
- Volatility: Consider the volatility of what you are trading. More volatile markets require a smaller trade size to maintain a safe level of risk. Evaluate historical price movements, average true range, and other volatility indicators to make an informed decision.
- Risk-reward ratio: Evaluate the potential risk-reward ratio of each trade. A higher ratio means you are potentially risking less for a greater reward. Also, aim for trades with suitable risk-reward profiles to increase your chances of profitability while keeping risk in check.
- Trade frequency: Determine how many trades you plan to take within a certain time frame. If you are trading multiple positions concurrently, adjust the size of position for each trade to ensure your overall risk exposure remains within your predetermined safe limits.
Build strategic trading plan and risk management with our 4 weeks incubator program.
How to Calculate Position Size in Forex?
Calculating the size of position in the forex market is an essential aspect of risk management and can greatly impact your trading success. Determining the appropriate trade size allows you to control your risk exposure and optimize potential gains. Let’s explore how to calculate position size in the forex market.
Position size is typically calculated based on three main factors: account balance, risk percentage, and the distance between the entry price and the stop-loss level. The risk percentage is a personal decision that reflects the maximum amount of capital you are willing to risk on a single trade. Let’s say you decide to risk 2% of your account balance per trade.
To calculate the position size, you can use the following formula:
Position Size = (Account Balance * Risk Percentage) / (Distance to Stop Loss* Pip Value)
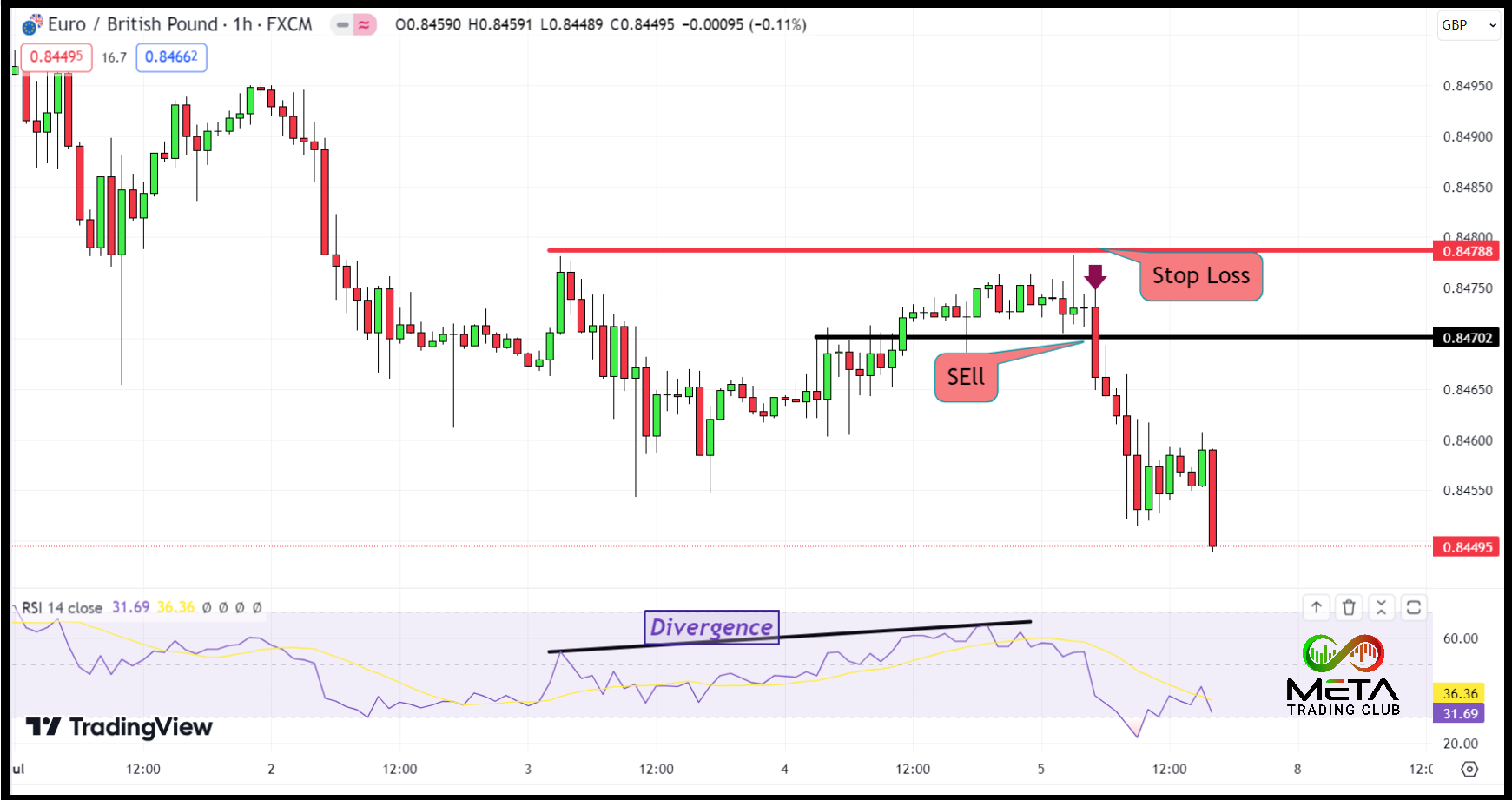
Let’s consider an example to illustrate this concept. Suppose your account balance is £10,000, and you’re willing to risk 2% (£200) on this trade. You decide to buy the EUR/GBP currency pair at 0.8470 and set your stop loss at 0.84790, resulting in a distance of 20 pips.
To calculate the pip value, you need to know the pip size of the currency pair you are trading. Let’s assume the pip value for the EUR/GBP pair is £10 for a standard lot (100,000 units). You can find out the pip value in forex calculators.
Using the formula, the position size would be:
Position Size = £10,000 * 0.02) / (20 pip * £10) = £200 / £200 = 1 standard lots
In this example, the appropriate position size for this trade would be 1 standard lot.
It’s important to note that trade size calculations may vary depending on your risk tolerance and trading strategy. Additionally, different brokers may have specific lot sizes or leverage options, so be sure to adapt the formula accordingly.
Final Words
As traders we all want big winning trades, it’s best to use position sizing strategies to ensure we can protect our trading capital. After all, we all want to be able to trade the next day (and that will be impossible if all your capital has been wiped out in a single trade).
And remember not to put all your eggs in one basket, That is not only about diversification, also include risk management and position sizing.
However, note that if you can’t sleep at night thinking about your open position, you are risking too much.
FAQs
- What is meant by position sizing?
This refers to the process of determining the appropriate number of shares, contracts, or units to trade based on your risk tolerance and the size of your trading account. It helps you manage risk and maximize returns by controlling the amount of capital allocated to each trade. - What is lot size and position size?
Lot size refers to the standardized quantity of stocks or that can be traded in a single transaction. Although, position size refers to the amount of capital you allocate to a specific trade. It’s calculated based on your risk tolerance and the distance between your entry price and stop-loss level. - What is position sizing techniques in trading?
Some effective strategies are fixed dollar risk value, fixed percentage risk value, volatility-based risks, contract size value and Kelly Criterion methods. - How do you calculate your position size?
Determine account risk and identify trade risk then, divide your account risk by the trade risk to find the proper trade size. - How to increase position size?
To increase the size of your position in trading, consider: Increase your trading account size by making profitable trades. Also, if you’re comfortable taking on more risk, you can allocate a larger portion of your account to each trade.