In the world of trading, scalp trading stands out as one of the most dynamic and exhilarating strategies. Designed for traders who thrive on quick decision-making and rapid market movements, scalp trading involves making numerous trades throughout the day to capitalize on small price fluctuations. This approach requires a keen eye, sharp reflexes, and a deep understanding of market trends. In this article, we’ll discover the essentials of scalp trading, explore proven techniques, and provide expert guidance to help you master this high-speed trading style. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or a newcomer looking to enhance your skills, our comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to succeed in the fast-paced arena of scalping.
Table of Contents
What Is Scalping?
Scalp trading is a fast-paced trading strategy aimed at profiting from small price changes in a stock or other financial instruments. Traders who use this strategy, known as scalpers, make numerous trades throughout the day, often holding positions for just a few seconds to minutes.
The main goal is to make small, quick profits in assets such as stocks, options, futures, Forex, crypto currencies and other securities. Also, scalpers may place anywhere from 10 to a few hundred trades in a single day. In addition, this strategy relies heavily on technical analysis, using tools like candlestick charts, moving averages, and momentum indicators.
Scalp trading requires a high level of market understanding, quick decision-making, and the ability to execute trades swiftly. It’s a challenging but potentially rewarding strategy for those who master it.
How Scalpers Make Decisions?
Scalpers make decisions based on a combination of parameters. Here’s a detailed look at how scalpers approach their trading:
Technical Analysis
Scalpers rely heavily on technical analysis to identify entry and exit points. They use various technical indicators and chart patterns to make quick decisions such as:
- Moving Averages: Help identify trends and potential reversal points.
- Candlestick Patterns: Provide insights into market sentiment and potential price movements.
- Momentum Indicators: Tools like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) help gauge the strength of price movements.
Real-Time Data
Scalpers need access to real-time data to make informed decisions quickly. This includes live price feeds, order book data, and market depth information. Also, real-time data allows scalpers to react instantly to market changes, ensuring they can capitalize on small price movements before they dissipate.
Market Conditions
Scalpers consider current market conditions, such as volatility and liquidity, to determine the best times to trade.
- Volatility: Higher volatility can provide more trading opportunities but also increases risk.
- Liquidity: High liquidity ensures that scalpers can enter and exit positions quickly without significant price slippage.
Risk Management
Effective risk management is crucial for scalpers to protect their capital and ensure long-term profitability.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Automatically close positions at predetermined loss levels to prevent significant losses.
- position sizing: Adjusting the size of trades based on risk tolerance and market conditions.
Psychological Discipline
Scalping requires a high level of psychological discipline to stick to trading plans and avoid emotional decision-making. Maintaining discipline helps scalpers avoid impulsive trades and ensures they follow their strategies consistently.
Automation
Many scalpers use automated systems or algorithms to execute trades based on predefined criteria. Benefits of this approach:
- Speed: Automated systems can execute trades faster than manual trading.
- Consistency: Reduces the impact of human emotions and errors.
Scalp Trading Strategies
Scalp trading involves making numerous trades throughout the day to profit from small price movements. Here are some effective scalp trading strategies:
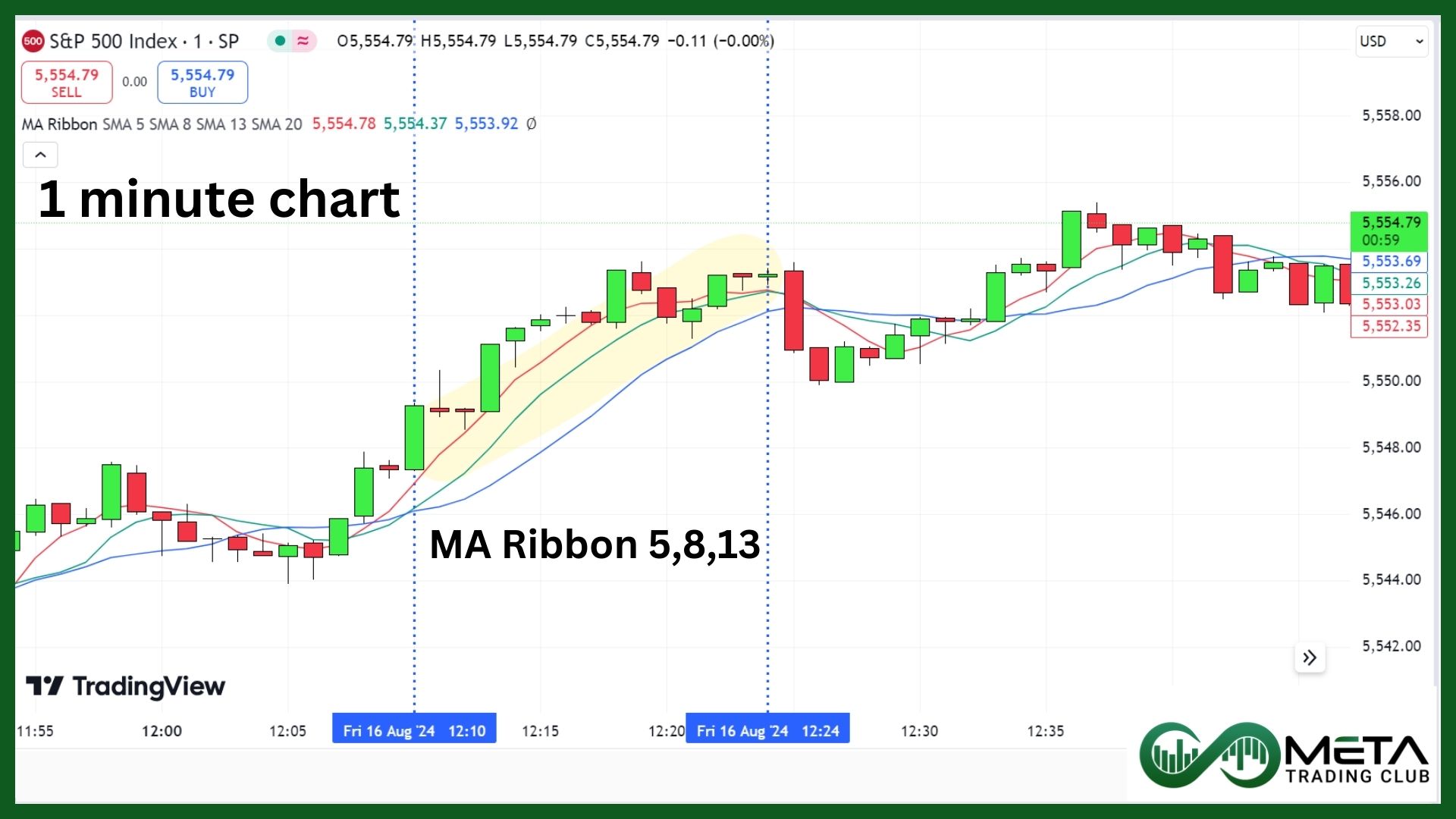
1. Moving Average Ribbon Entry Strategy
The moving average ribbon entry strategy is a popular scalping technique that helps traders identify strong trends and potential entry points. A moving average ribbon consists of multiple moving averages of different lengths plotted on the same chart. These moving averages create a ribbon-like appearance, helping traders visualize the strength and direction of a trend.
Also, the moving average ribbon entry strategy is a powerful tool for scalpers, helping to identify trends and make informed trading decisions. By using multiple moving averages, traders can gain a clearer picture of market dynamics and improve their chances of successful trades.
How to Use the Moving Average Ribbon in Scalping?
Identify Trend Direction:
- Uptrend: When the moving averages are aligned in ascending order (shorter-term MAs above longer-term MAs) and angled upwards, it indicates a strong uptrend.
- Downtrend: When the moving averages are aligned in descending order (shorter-term MAs below longer-term MAs) and angled downwards, it indicates a strong downtrend.
Set Up the Moving Average Ribbon:
- Select Moving Averages: Choose a series of moving averages with different periods. A common setup includes 5, 8, and 13-period simple moving averages (SMAs).
- Plot on Chart: Plot these moving averages on a short-term chart, such as a 1-minute or 2-minute chart.
Entry Signals:
- Bullish Crossover: In an uptrend, look for entry signals when the shorter-term moving averages cross above the longer-term moving averages.
- Bearish Crossover: In a downtrend, consider entering a trade when the shorter-term moving averages cross below the longer-term moving averages.
Trend Confirmation:
- Ribbon Expansion: When the ribbon expands (moving averages spread apart), it confirms a strengthening trend.
- Ribbon Contraction: When the ribbon contracts (moving averages come closer together), it may indicate a pullback or potential trend reversal.
Example
Imagine you have an S&P 500 chart with 5, 8, and 13-period moving averages. For example, if the 5-period MA crosses above the 8-period MA, and both are above the 13-period MA, this alignment suggests a strong uptrend. You might enter a long position at this point, aiming to profit from the continued upward movement.
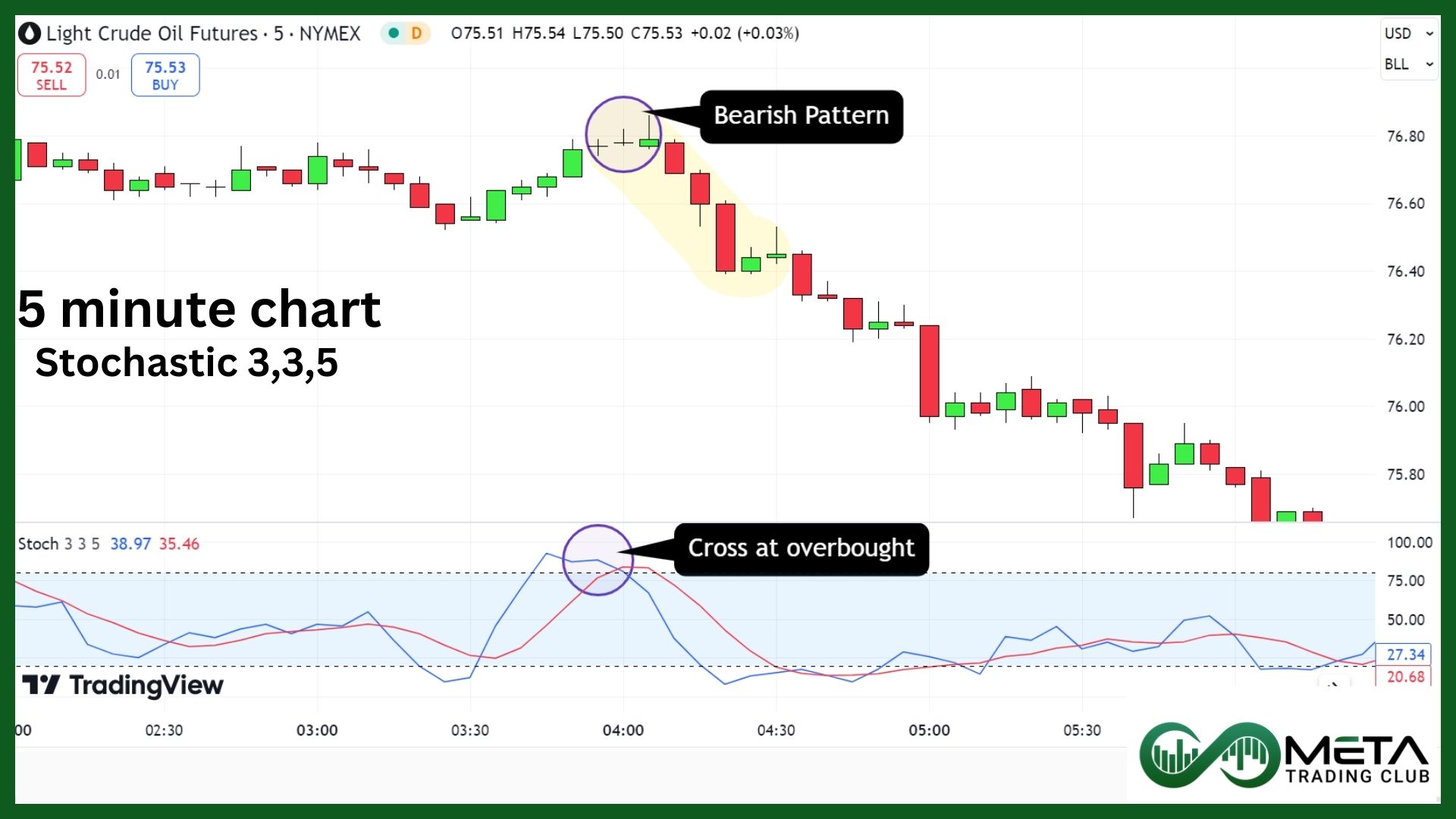
2. Stochastic Oscillator Strategy
The stochastic oscillator strategy is a popular technique among scalpers for identifying overbought and oversold conditions, which can signal potential entry and exit points.
Also, the stochastic oscillator strategy is a powerful tool for scalpers, using the 5, 3, 3 settings and combining them with candlestick patterns and trend analysis, traders can enhance their chances of making profitable trades.
What is the Stochastic Oscillator?
The stochastic oscillator is a momentum indicator that compares a security’s closing price to its price range over a specific period. It consists of two lines:
- %K Line: The main line that measures the current closing price relative to the high-low range over a set period.
- %D Line: A moving average of the %K line, providing a signal line for crossovers.
How to Use the Stochastic Oscillator in Scalping?
Determine the Market Trend:
Use a higher timeframe chart (like 1-hour or 4-hour) to identify the overall market trend. This helps avoid trading against the trend.
Identify Potential Trade Setups:
Switch to a lower time frame chart (such as 1-minute or 5-minute) to look for trade setups. One popular setup is the bullish or bearish divergence, where the Stochastic Oscillator makes a higher low while the price makes a lower low, or vice versa.
Set Up the Stochastic Oscillator:
For scalping, the most commonly used settings are 5, 3, and 3 for the %K and %D lines. Apply the Stochastic Oscillator with the 5, 3, 3 settings to your chart.
Buy Signal:
Wait for the Stochastic Oscillator to move into the oversold region (below 20 on the scale). Look for a bullish reversal pattern or signal, such as a hammer or bullish engulfing candlestick pattern. Confirm the bullish reversal signal with a bullish crossover on the Stochastic Oscillator, where the %K line crosses above the %D line within the oversold region.
Sell Signal:
Wait for the Stochastic Oscillator to move into the overbought region (above 80 on the scale). Look for a bearish reversal pattern or signal, such as a shooting star or bearish engulfing candlestick pattern. Confirm the bearish reversal signal with a bearish crossover on the Stochastic Oscillator, where the %K line crosses below the %D line within the overbought region.
Example
Imagine you’re trading a crude oil future on a 5-minute chart. The Stochastic Oscillator moves above 80, indicating an overbought condition. You notice a Hanging man pattern forming, and shortly after, the %k line crosses below the %D line. This alignment suggests a potential selling opportunity, and you enter a short position.
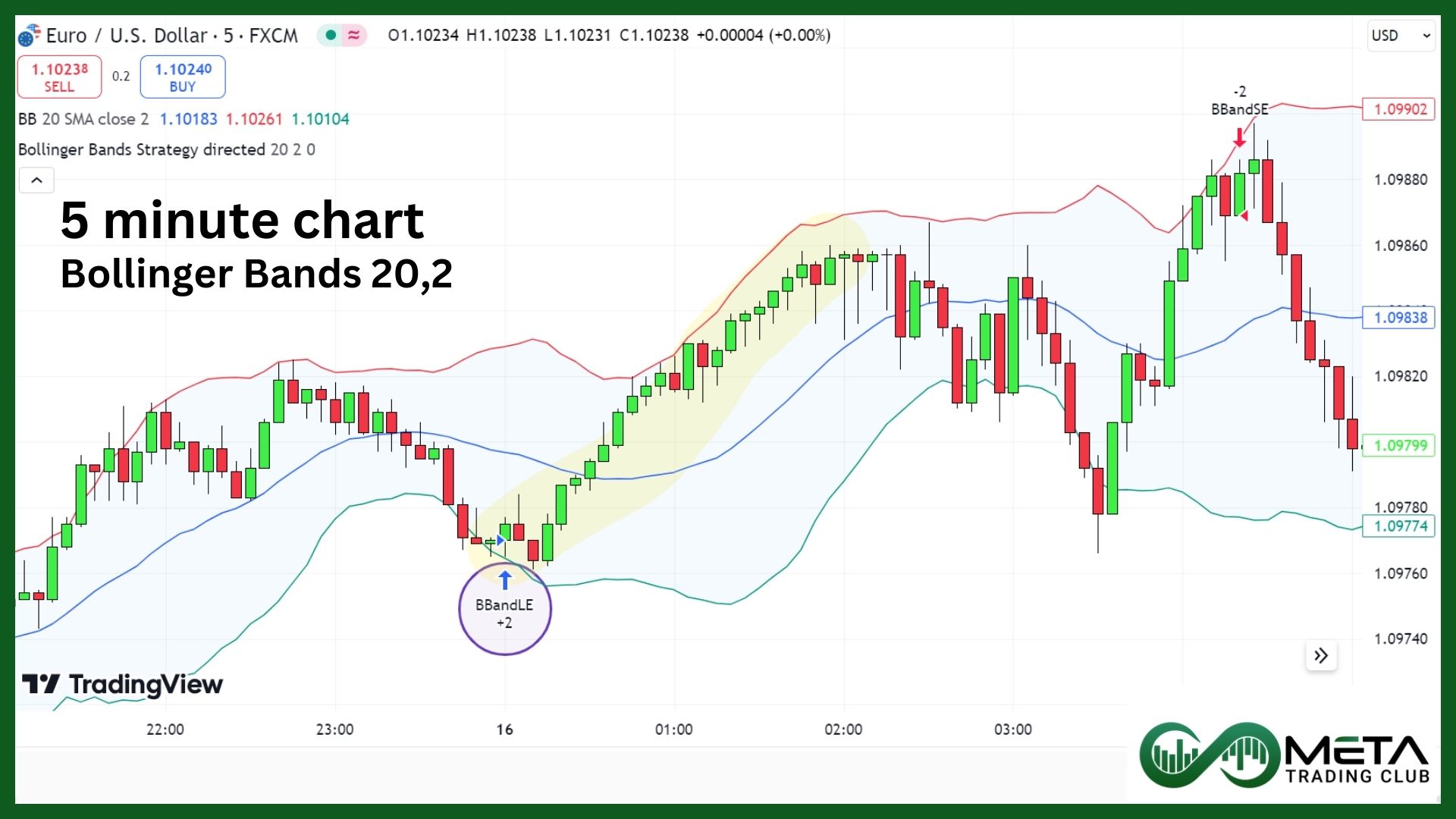
3. Bollinger Bands Strategy
The Bollinger Bands strategy is a popular technique among scalpers for identifying potential entry and exit points based on market volatility. The Bollinger Bands strategy is a powerful tool for scalpers, using Bollinger Bands in conjunction with candlestick patterns and trend analysis, traders can enhance their chances of making profitable trades.
What are Bollinger Bands?
Bollinger Bands are a technical analysis tool developed by John Bollinger. They consist of three lines:
- Middle Band: A simple moving average (SMA), typically set to 20 periods.
- Upper Band: Calculated by adding two standard deviations to the middle band.
- Lower Band: Calculated by subtracting two standard deviations from the middle band.
These bands dynamically adjust to market conditions, expanding during periods of high volatility and contracting during periods of low volatility.
How to Use Bollinger Bands in Scalping?
Identify Market Conditions:
- Trending Market: In a trending market, prices tend to stay close to the upper or lower bands.
- Range-Bound Market: In a range-bound market, prices oscillate between the upper and lower bands.
Set Up the Bollinger Bands:
- Select the Timeframe: Use a short timeframe, such as a 1-minute or 5-minute chart, to align with the quick nature of scalping.
- Apply Bollinger Bands: Set the Bollinger Bands with a 20-period SMA and 2 standard deviations.
Entry Signals:
- Buy Signal: In an uptrend, wait for the price to touch or slightly penetrate the lower Bollinger Band. Look for a bullish candlestick pattern (such as hammer or bullish engulfing) to confirm the entry.
- Sell Signal: In a downtrend, wait for the price to touch or slightly penetrate the upper Bollinger Band. Look for a bearish candlestick pattern (like shooting star or bearish engulfing) to confirm the entry.
Exit Signals:
- Take Profit: Consider taking profit when the price moves back towards the middle band or reaches the opposite band.
- Stop Loss: Place a stop loss just beyond the recent swing high or low to manage risk.
Example
Imagine you’re trading a EUR/USD currency pair on a 5-minute chart. The price touches the lower Bollinger Band in an uptrend, and you notice a bullish pattern forming. This alignment suggests a potential buying opportunity. You enter a long position and set your take profit near the middle band, with a stop loss just below the recent swing low.
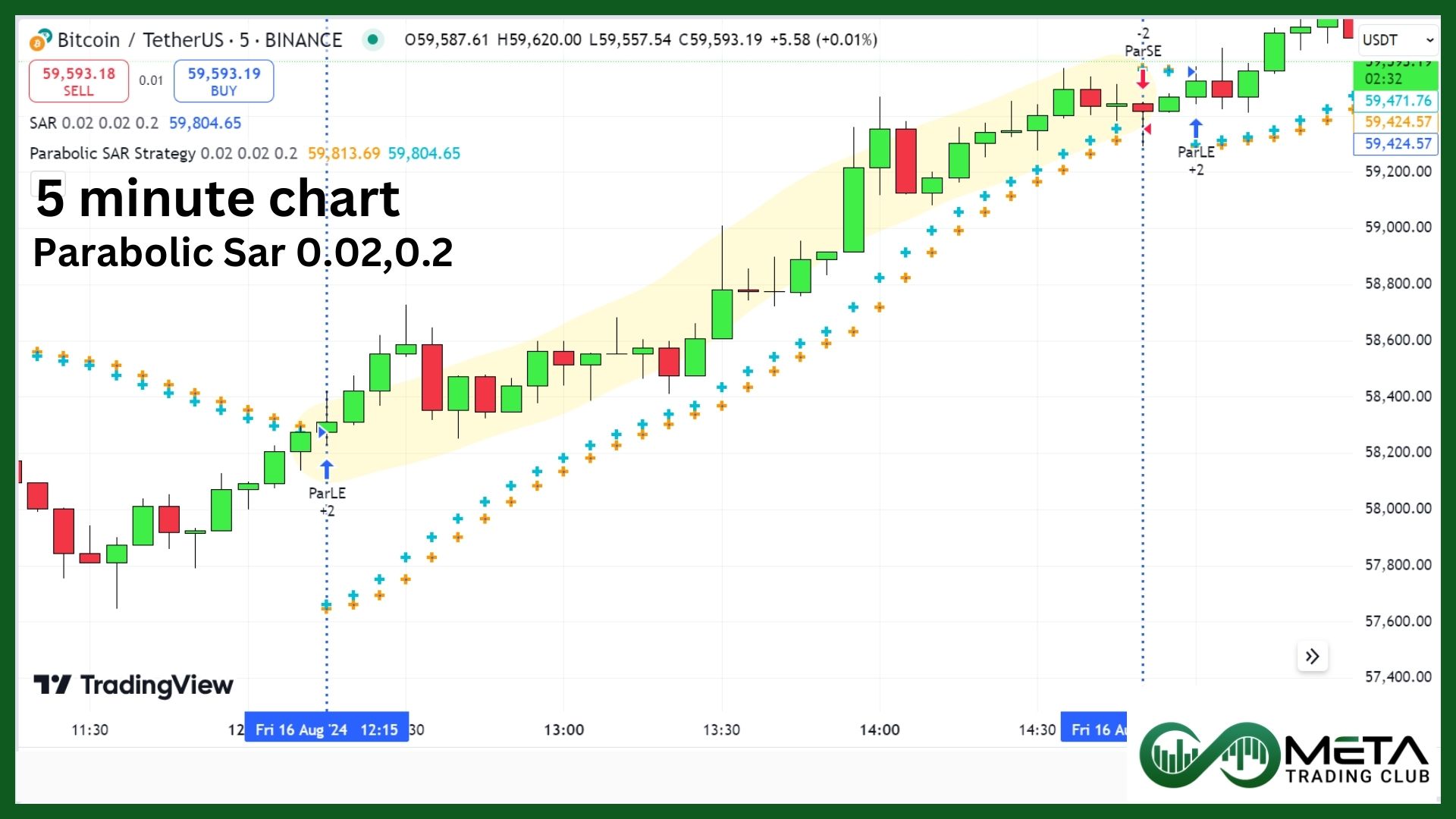
4. Parabolic SAR Strategy
The Parabolic SAR (Stop and Reverse) Strategy is a popular technique among scalpers for identifying potential entry and exit points based on trend direction and reversals. Also, using the Parabolic SAR in conjunction with other technical indicators and trend analysis, traders can enhance their chances of making profitable trades.
What is the Parabolic SAR?
The Parabolic SAR is a trend-following indicator developed by J. Welles Wilder. It consists of dots placed above or below the price, indicating the direction of the trend:
- Dots below the price: Indicate an uptrend.
- Dots above the price: Indicate a downtrend.
How to Use the Parabolic SAR in Scalping?
Identify Trend Direction:
- Uptrend: When the dots are below the price, it indicates an uptrend. Look for buying opportunities.
- Downtrend: When the dots are above the price, it indicates a downtrend. Look for selling opportunities.
Parabolic SAR Set Up:
- Select the Timeframe: Use a short timeframe, such as a 1-minute or 5-minute chart, to align with the quick nature of scalping.
- Apply the Parabolic SAR: Use the default settings (Step: 0.02, Maximum: 0.2) or adjust based on your preference and market conditions.
Entry Signals:
- Buy Signal: Enter a long position when the dots move from above to below the price, indicating a potential trend reversal to the upside.
- Sell Signal: Enter a short position when the dots move from below to above the price, indicating a potential trend reversal to the downside.
Exit Signals:
- Take Profit: Consider taking profit when the dots switch sides again, indicating a potential trend reversal.
- Stop Loss: Place a stop loss just beyond the recent swing high or low to manage risk.
Example
Imagine you’re trading a crypto currency pair BTC/USDT on a 5-minute chart. The Parabolic SAR dots move from above to below the price, indicating a potential uptrend. You enter a long position and set your take profit when the dots move back above the price, with a stop loss just below the recent swing low.
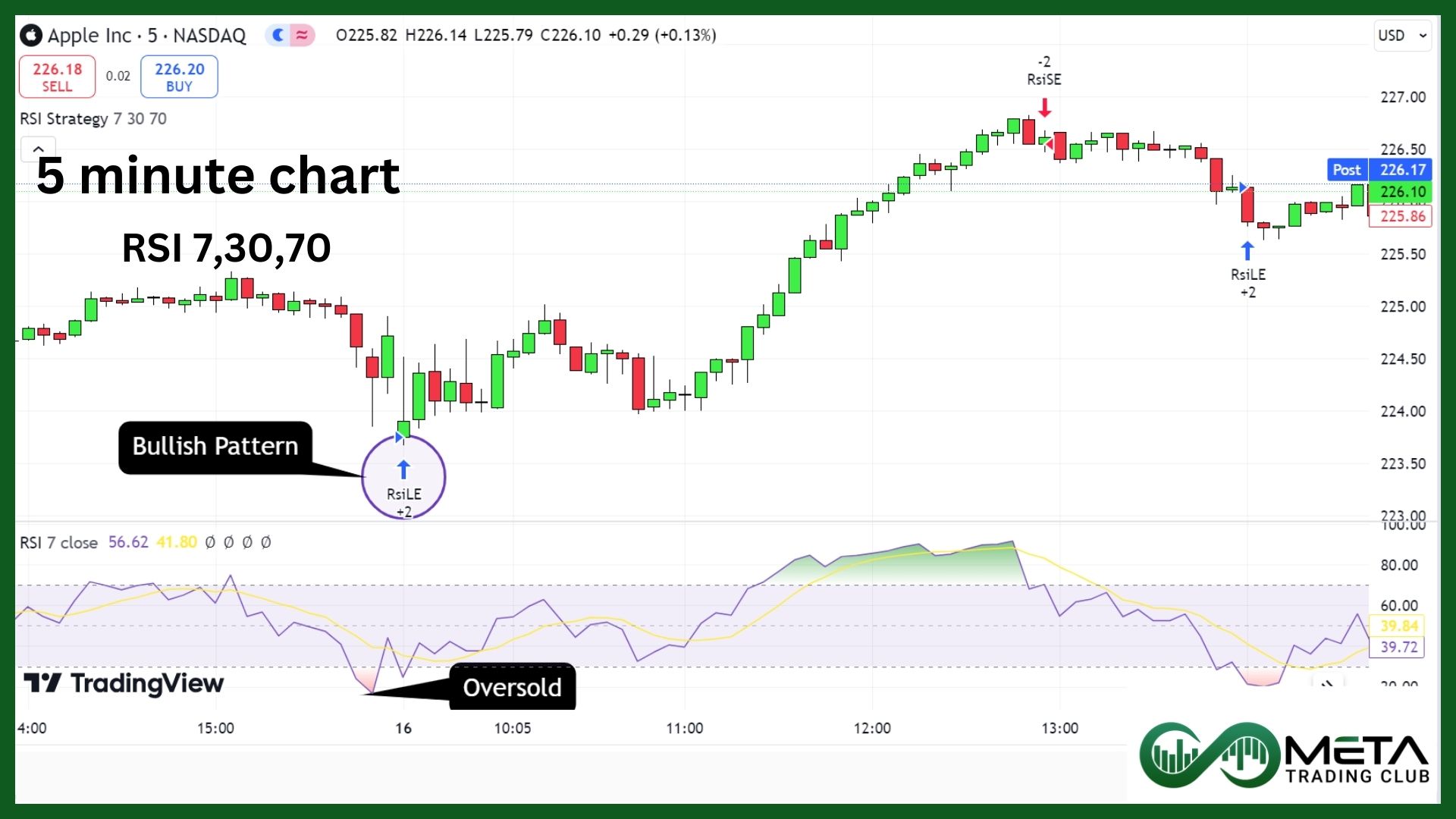
5. The RSI (Relative Strength Index) Strategy
The RSI (Relative Strength Index) Strategy is a popular technique among scalpers for identifying overbought and oversold conditions, which can signal potential entry and exit points.
Also, the RSI strategy is a powerful tool for scalpers, using the RSI with appropriate settings and combining it with candlestick patterns and trend analysis, traders can enhance their chances of making profitable trades.
What is the RSI?
The RSI is a momentum oscillator developed by J. Welles Wilder. It measures the speed and change of price movements on a scale from 0 to 100. Typically, readings above 70 indicate overbought conditions, while readings below 30 indicate oversold conditions.
How to Use the RSI in Scalping?
Determine the Market Trend:
Use a higher time frame chart (like 1-hour or 4-hour) to identify the overall market trend. This helps avoid trading against the trend.
Identify Potential Trade Setups:
Switch to a lower time frame chart (such as 1-minute or 5-minute) to look for trade setups. One popular setup is the bullish or bearish divergence, where the RSI makes a higher low while the price makes a lower low, or vice versa.
Set Up the RSI:
For scalping, the RSI is often set to a shorter period to increase sensitivity. Common settings include a 7-period RSI with overbought and oversold levels set at 70 and 30, respectively. Apply the RSI with the chosen settings to your chart.
Buy Signal:
Wait for the RSI to move into the oversold region (below 30 on the scale). Look for a bullish reversal pattern or signal, such as a hammer or bullish engulfing candlestick pattern. Confirm the bullish reversal signal with a bullish crossover on the RSI, where the RSI moves back above the 30 level.
Sell Signal:
Wait for the RSI to move into the overbought region (above 70 on the scale). Look for a bearish reversal pattern or signal, such as a shooting star or bearish engulfing candlestick pattern. Confirm the bearish reversal signal with a bearish crossover on the RSI, where the RSI moves back below the 70 level.
Example
Imagine you’re trading Apple (AAPL) on a 5-minute chart. The RSI moves below 30, indicating an oversold condition. You notice a bullish pattern forming, and shortly after, the RSI moves back above 30. This alignment suggests a potential buying opportunity, and you enter a long position.
What You’ll Need to Execute Scalp Trades
To successfully execute scalp trades, you’ll need a combination of tools, technology, and skills. Here’s a comprehensive list of what you’ll need:
Technical Analysis Tools
- Charts: Use 1-minute or 5-minute charts to monitor price movements closely.
- Indicators: Common indicators include moving averages, Bollinger Bands, RSI, and MACD.
- Candlestick Patterns: Recognize patterns that indicate potential price reversals or continuations.
Real-Time Data Tools
- Live Price Feeds: Ensure you have a reliable source for real-time price updates.
- Level II Quotes: Provides detailed information about the order book, showing the depth of market orders.
- Time and Sales: Track the actual transactions happening in the market to gauge momentum.
Fast Execution Platform Features
- Low Latency: Choose a platform known for fast execution speeds.
- Direct Market Access (DMA): Allows you to place orders directly on the exchange, reducing delays.
- Hotkeys: Use keyboard shortcuts to enter and exit trades swiftly.
Reliable Broker
Your broker should support your scalping strategy with low fees and tight spreads.
- Low Commissions: High-frequency trading can lead to significant transaction costs.
- Tight Spreads: Ensure the broker offers competitive spreads to maximize your profit margins.
- Reputation for Speed: Choose a broker known for fast order execution.
Risk Management Tools
- Stop-Loss Orders: Automatically close positions at predetermined loss levels.
- Position Sizing: Adjust the size of your trades based on your risk tolerance.
- Reward-Risk Ratio: Maintain a favorable reward-risk ratio to ensure long-term profitability.
Psychological Skills
- Emotional Control: Stay calm and composed, even during volatile market conditions.
- Patience: Wait for the best trading opportunities and avoid impulsive trades.
- Consistency: Follow your trading strategy consistently to achieve steady results.
Automation Tools
- Trading Algorithms: Use algorithms to execute trades based on predefined criteria.
- Bots: Automated trading bots can operate continuously, taking advantage of trading opportunities even when you’re not actively monitoring the market.
Scalping vs Day Trading
Scalping is a specific type of day trading, but it has distinct characteristics that set it apart from other day trading strategies. Here are the key differences:
- Trade Duration
Scalpers hold positions for very short periods, typically seconds to minutes. The goal is to make small profits from minor price movements. But day traders may hold positions for several minutes to hours, but always close them within the same trading day. - Trade Frequency
Scalpers execute a high volume of trades throughout the day, sometimes making hundreds of trades. But day traders typically make fewer trades, focusing on larger price movements and fewer transactions. - Profit Targets
The profit target for each trade is small for scalpers, often just a few cents or a fraction of a percent. Scalpers rely on the accumulation of many small gains. But day traders often aim for larger profit margins per trade, which can be several percent. - Risk Management
Scalpers minimize risk by holding positions for very short periods, reducing exposure to market volatility. But day traders manage risk by using stop-loss orders and position sizing, but their longer holding periods can expose them to more market fluctuations. - Market Analysis
Scalpers primarily use technical analysis, focusing on real-time data, price action, and short-term indicators. Day traders not only use technical analysis, but also may incorporate fundamental analysis and news events to inform their decisions. - Stress and Intensity
Scalping is highly intensive and requires constant attention and quick decision-making. The fast-paced nature can lead to higher stress levels. Day trading, while still demanding, may allow for slightly more relaxed decision-making processes due to longer trade durations.
Scalping is a unique form of day trading characterized by its short trade durations, high frequency of trades, small profit targets, and reliance on technical analysis.
Advantages of Scalp Trading
Scalp trading offers several advantages that can make it an appealing strategy for scalpers:
- Quick Profits
Scalping focuses on capturing small price movements, often just a few ticks. By executing a high volume of trades, scalpers can accumulate these small profits over time. Also, this allows traders to see immediate returns on their trades, which can be particularly satisfying and motivating. - Limited Market Exposure
Scalpers hold positions for very short periods, typically seconds to minutes. This minimizes their exposure to market risks, such as sudden news events or significant price swings that can occur over longer time frames. So, this can lead to more stable and predictable trading outcomes. - Frequent Trading Opportunities
Scalping takes advantage of the numerous small price movements that occur throughout the trading day. This provides traders with many opportunities to enter and exit trades. Also, this constant activity can also help traders stay sharp and improve their skills over time. - High Win Rate
Scalpers often aim for small, achievable price targets, which can result in a higher ratio of winning trades compared to losing ones. The focus on small gains means that trades are more likely to hit their profit targets. Also, a high win rate can boost trader confidence and contribute to consistent profitability. - Less Influence from Market Trends
Scalping is less dependent on broader market trends and more focused on short-term price movements. This means that scalpers can profit in various market conditions, whether the market is trending up, down, or sideways. - Utilization of High LeverageScalpers can use high leverage to amplify their gains from small price movements. Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. While leverage increases potential profits, it also magnifies potential losses. However, when used carefully, leverage can significantly enhance the profitability of scalping.
Disadvantages of Scalp Trading
Scalping, while potentially profitable, comes with several disadvantages that traders should be aware of:
- Time-Consuming
Scalping requires traders to be glued to screens for extended periods, maybe the entire trading day. This is because scalping involves making numerous trades within short time frames, sometimes just seconds or minutes apart. - High Stress and Emotional Pressure
The fast-paced nature of scalping means that traders must make rapid decisions under pressure. The need to constantly monitor the market and execute trades quickly can lead to high levels of stress. So, It requires strong emotional control to avoid making impulsive decisions. - Transaction Costs
Scalping involves a high volume of trades, which means that transaction costs, such as commissions and fees. Even if each trade incurs a small fee, the cumulative cost can be significant. These costs can reduce overall profitability. - Limited Profit Potential
Since scalping focuses on small price movements, the profit per trade is usually minimal. Scalpers aim to make a small profit from each trade, which means they need to execute a large number of successful trades to achieve substantial profits. - Intense Focus and Discipline
Scalping demands intense focus and discipline. Traders must be able to stick to their strategies and exit trades quickly to avoid losses. However, this requires a high level of concentration and the ability to follow a strict trading plan without deviation. Any lapse in concentration or discipline can lead to significant losses, as scalping leaves little room for error. - Risk of Large Losses
One of the biggest risks in scalping is that a single large loss can wipe out the many small gains that a trader has accumulated. This is because scalp trading involves frequent trades with small profit margins, so a significant loss can have a disproportionate impact. This makes risk management crucial in scalping.
Final Words
Scalp trading demands quick thinking, precise execution, and a thorough understanding of market dynamics. However, for those who master this fast-paced trading style, the rewards can be substantial. By employing the strategies and techniques discussed in this article, you can enhance your trading performance and capitalize on the numerous opportunities that scalp trading presents. Remember, consistency and discipline are key to success in this high-speed trading environment.
As you embark on your scalp trading journey, keep in mind that continuous learning and adaptation are crucial. The market is ever-evolving, and staying informed about the latest trends and strategies will give you a competitive edge. Boost your trading skills by participating in our Incubator program. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced trader, the insights shared here aim to equip you with the knowledge and confidence to thrive in the world of scalp trading.
FAQs
Scalping is a trading strategy that aims to profit from small price changes in financial markets. Traders, known as scalpers, make numerous trades throughout the day, holding positions for very short periods, often just seconds or minutes. The goal is to accumulate many small gains that can add up to significant profits.
Scalping can be profitable, but it requires a lot of skill, discipline, and quick decision-making. Profits per trade are usually small, so scalpers rely on high trading volumes and tight spreads.
Stock scalping, in the context of trading, is generally legal. However, illegal stock scalping refers to the deceptive practice of recommending others to buy a security while secretly selling the same security. This is closely monitored by regulatory bodies like the SEC.
1-minute scalping can be effective for experienced traders who can make quick decisions and manage risk well. It offers frequent trading opportunities and the potential for small, consistent profits. However, it also comes with high transaction costs and requires intense focus and discipline.
Scalping is a form of trading, but it can be more challenging due to its fast-paced nature. It requires quick decision-making, constant market monitoring, and the ability to handle high stress.